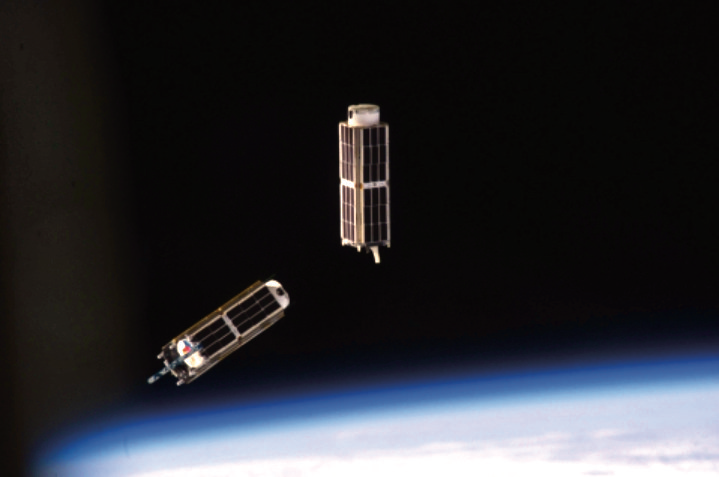
SMC deploys Aerospace’s Rogue smallsat from ISS
Mission accomplished on behalf of the U.S. Space Force’s Space and Missile Systems Center and its mission partners as they successfully deployed Aerospace’s Rogue Alpha and Rogue Beta CubeSats from the Northrop Grumman Cygnus capsule at 1 p.m. and 4:10 p.m. respectively, on January 31, 2020, marking the beginning of the program’s mission experiment plan.
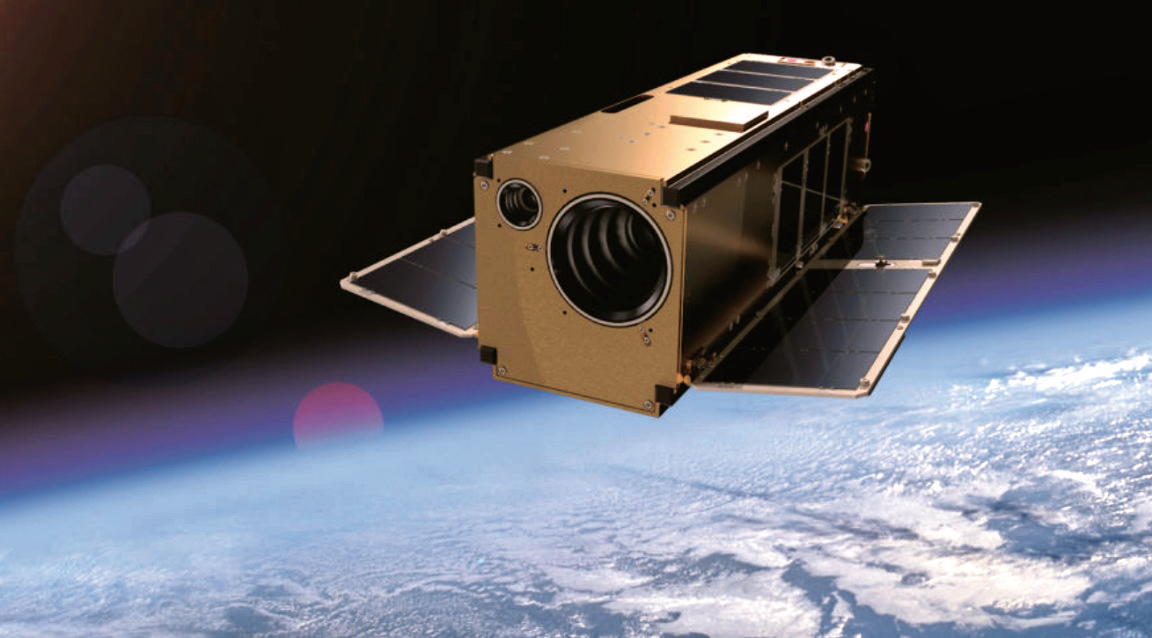

The plan involves the two satellites using their short-wave infrared sensors to create a baseline for processing cloud backgrounds and inform future Low Earth Orbit satellites.
The U.S. Air Force will also use this program’s unclassified data to investigate potential uses of the capability.

Colonel Dennis Bythewood, Program Executive Officer for Space Development, said that the Space and Missile Systems Center is proud of this team’s accomplishments and the speed at which this program developed.
The cubedats were designed, built, and tested by The Aerospace Corporation, a national nonprofit corporation that operates as a federally funded research and development center dedicated to advancing the nation’s missions in space.
Jeff Emdee, general manager of the Space Development Division at The Aerospace Corporation said each three-unit cubesat is about the size of a shoe box and contains both visible and infrared sensing, as well as a laser communications downlink, that will allow them to explore operations in low Earth orbit to benefit future system concepts.
Satellite SVN-74 healthy and active
Setting SVN-74 healthy and active means the satellite will be available for use by military and civilian GPS users around the world as part of the constellation currently maintained by the squadron.

Second Lt. Kelley McCaa, 2nd Space Operations Squadron
satellite vehicle operator, and Airman 1st Class John Garcia,
2nd SOPS satellite systems operator, set satellite vehicle
number-74 as healthy and active to users, January 13, 2020,
Schriever Air Force Base, Colorado.
USAF photo by Staff Sgt. Matthew Coleman-Foster.
This makes the satellite the first iteration in the GPS III family to join the active constellation following its launch December 23, 2018.
Captain Ryan Thompson, 2nd SOPS assistant director of sustainment, said various training modules and upgrades were instrumental in making the satellite operational. “In order to operate GPS III, we first had to install Architecture Evolution Plan 8.0,” he said.
“This allowed our squadron to control the new satellite without a next generation operational control system. The 2nd SOPS training and evaluations flight was able to expeditiously give our operators top-up training that allowed them to become comfortable with the new satellite.”
The GPS III vehicle family provides new capabilities vital to ensuring the fidelity of the constellation and signal in the contested, degraded and operationally limited environments.
According to the Lockheed-Martin press release, GPS III satellites have three times better accuracy and as much as eight times improved anti-jamming capabilities than their predecessors, and a design life extending 25 percent longer than the newest GPS satellites on-orbit today.
GPS III’s new civil signal will also make it the first GPS satellite to broadcast a compatible signal with other international global navigation satellite systems, such as Galileo, improving connectivity for civilian users.
2nd SOPS is already preparing for the second GPS Block III vehicle in orbit, awaiting its day to become healthy and active.

“There are vehicles currently projected to be put into the constellation and then, following this, there will be the Block III-F follow-on vehicles,” said Captain Kaoru Elliot, 2nd SOPS assistant Director of Operations. “With those vehicles in place, all of those capabilities will come into the next decade.”
A third vehicle for GPS III is scheduled for launch later this year. “It [GPS Block III vehicle two] is being managed currently by Lockheed-Martin,” Elliott said.
“They are the ones actually getting the satellites up there and, once it is up in orbit, they make certain everything is good before handing it over to us.”
Story by Staff Sgt. Matthew Coleman-Foster, 50th Space Wing
Multi-purpose, airborne terminal debuts from Orbit Communications
Orbit Communication Systems Ltd. (TASE: ORBI) has developed a new, Ka-band, multi-purpose, airborne terminal.
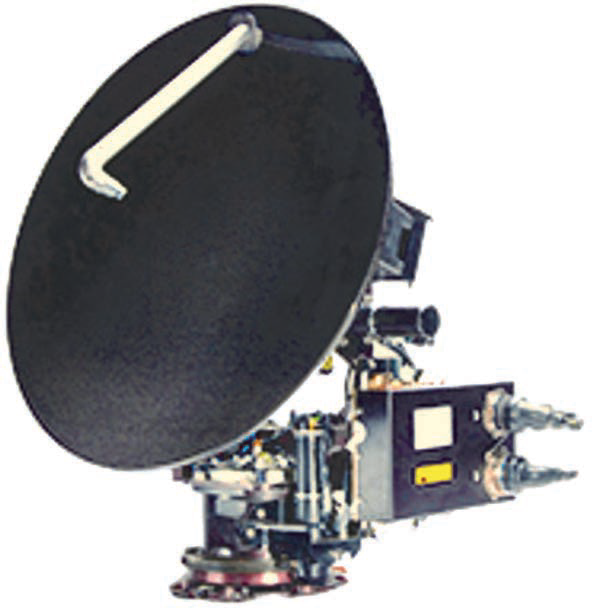

The compact Multi-Purpose Terminal (MPT) 30WGX, featuring a 30 cm. (12-inch) antenna, will be able to deliver high-throughput wideband communications via the Inmarsat Global Xpress worldwide network for a broad range of airborne platforms. Built to fulfill “anytime, anywhere” connectivity requirements, the lightweight, small-footprint terminal combines high performance with Orbit’s reliability to address new opportunities in military aircraft and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs).
Following certification, volume production of the 30WGX terminal is planned for Orbit’s U.S.-based facilities. Orbit’s MPT 30WGX terminal complements the company’s 46 cm. (18-inch) MPT 46WGX terminal, which will shortly enter full-scale production.
Once certified, it will be similarly optimized for use with Inmarsat’s Global Xpress system and will be interoperable with military Ka-band services, affording unique capabilities and flexibility.
Stav Gizunterman, VP of Sales and Marketing at Orbit, said the company is very pleased to be partnering with Inmarsat to develop innovative new airborne capabilities. This new terminal, which complements the firm’s MPT 46WGX, will help open up service offerings to an expanded range of aircraft.
Steve Gizinski, CTO, Inmarsat Government, added that the company is pleased to be working with Orbit to introduce innovative and forward-looking satellite solutions that support today’s complex missions. Orbit’s innovation and expansion of their MPT terminal line ensure that airborne users will have access to reliable wideband mobility for increased agility and worldwide portability.
U.S. DoD contractor orders Comtech EF Data satellite modems
During Q2 of fiscal 2020, Comtech Telecommunications Corp. (NASDAQ: CMTL) announced that their Tempe, Arizona-based subsidiary, Comtech EF Data Corp. (part of Comtech’s Commercial Solutions segment), received a $2.9 million order for satellite modems from a major U.S. Department of Defense (“DoD”) contractor.

The order specified the DMD2050E MIL-STD-188-165A/STANAG 4486 Edition 3 Compliant Universal Satellite Modem, which will be used to support the U.S. Army Project Manager (PM) Tactical Network.
The DMD2050E Satellite Modem is designed to comply with the widest possible range of U.S. Government and commercial standards and is compatible with the largest number of satellite modems in the industry.
The modem is fully compliant with MIL-STD-188-165A (all terminal types), fully complies with STANAG 4486 Edition 3, as well as the IESS- 308, IESS-309, IESS-310 and IESS- 315 commercial standards.
Maxar’s SecureWatch GEOINT platform has Netherlands MOD contract
Maxar Technologies (NYSE:MAXR) (TSX:MAXR) has revealed that the Defence Geographic Agency (DGeo) of The Netherlands Ministry of Defence signed a multi-million dollar, multi-year subscription to SecureWatch, the company’s cloud-based geospatial intelligence (GEOINT) platform.
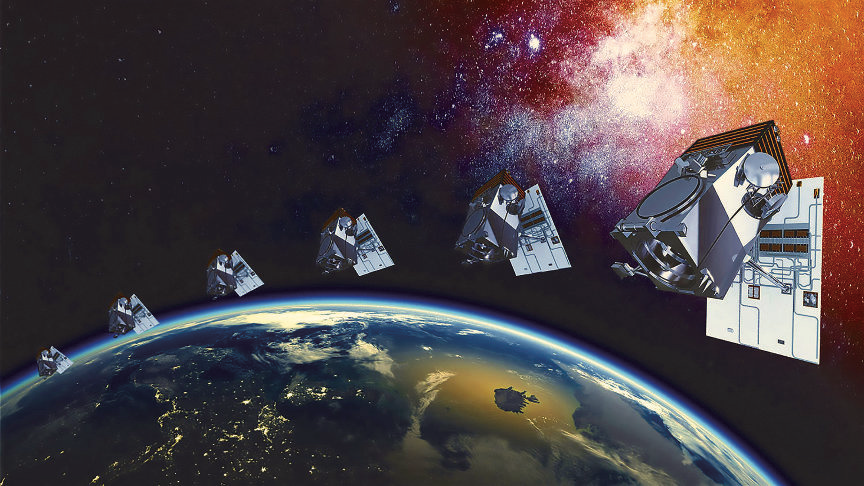

Artistic rendition of World View Legion satellites on-orbit.
Image is courtesy of Maxar.
DGeo will leverage SecureWatch to enrich its geospatial foundation data holdings and derivative product portfolio that aid critical decisionmaking within The Netherlands Ministry of Defence (MoD).
Through SecureWatch, DGeo will have access to Maxar’s 110- petabyte, high-resolution satellite imagery library, daily imagery collections, Vivid and Metro imagery mosaics, FirstLook service and synthetic aperture radar data from MDA’s RADARSAT-2 satellite.
When the WorldView Legion constellation imagery is available after the first satellites launch in early 2021, DGeo will also access it via SecureWatch.
The abundance and variety of geospatial data available in SecureWatch will inform and support the MoD’s information-driven activities such as mission planning, disaster response and border security, among other purposes.
Tony Frazier, Maxar’s Executive Vice President of Global Field Operations, said Maxar is delighted to bring DGeo and the Dutch MoD ecosystem into SecureWatch’s evergrowing community of subscribers.

As one of the largest SecureWatch awards to date, this contract is the culmination of a careful consultation process with DGeo, ensuring that Maxar’s solution has the greatest impact on their work. SecureWatch, with its mission-centric design and depth of content, fits DGeo’s requirements perfectly.
Lieutenant Colonel Rijk van Hunnik, DGeo’s Commanding Officer, noted that SecureWatch will facilitate DGeo’s ability to bring geospatial insights to a broader community within the Dutch MoD.
The Lieutenant Colonel added that secure, on-demand and easy access to very high-resolution imagery promises to be a game-changer for the organization's decision-making process and operations, allowing for the allocation of resources in the most effective way possible.