Harris Provides U.S. Army with Comms
Harris Corporation has been selected to outfit U.S. Army Security Force Assistance Brigades (SFABs) with reliable and combat-proven communication systems.

Harris’ Falcon III® AN/PRC-117G(V)1(C) Multiband Networking Manpack Radio.
Harris will provide a full battlefield solution including its Falcon III® AN/PRC-152A Wideband Networking Handheld Radios and AN/PRC-117G Multiband Networking Manpack Radios, as well as its AN/PRC-160 High Frequency Manpack Radios.
The radios will be equipped with the Soldier Radio Waveform (SRW) and the Adaptive Networking Wideband Waveform (ANW2), providing robust battlespace communications.
The SFAB trains and organizes coalition forces, while equipping them with proven and reliable equipment needed to complete their missions.
The SFAB builds coalition partner capability, preserving U.S. Army combat forces for other pressing missions if required.
Chris Young, the President at Harris Communication Systems, said that the Security Force Assistance Brigades are an important, near-term Army priority. Harris’ world-class manufacturing facility enables the firm to quickly support the Army with immediate delivery of these battle-tested radios and waveforms, providing the critical communications capability for these brigades on the battlefield.
www.harris.com
Space and Missile Defense Command Leads the U.S. Army Into space
For Soldiers looking to take their career to the ultimate height — literally — the U.S. Army Space and Missile Defense Command/Army Forces Strategic Command oversees Functional Area 40, or FA40, the space operations officer and Army space cadre development and management selection for Soldiers looking to transition to a career in space.

A U.S. Army uniform featuring an Army Master Space Badge. Photo is courtesy of Carrie David Campbell.
“FA40 officers serve in operating and generating force positions supporting the Army and unified action partners that focus on delivering space capabilities to the warfighter today, as well as developing and integrating space capabilities for the future,” said Mike Connolly, director, USASMDC/ARSTRAT Army Space Personnel Development Office,
or ASPDO.
Soldiers are selected for the FA40 after a competitive selection process through the Voluntary Transfer Incentive Program, or VTIP, which can occur at the four-year mark of a Soldier’s career. In addition to their technical abilities, Soldiers applying for the FA40 are also evaluated based on their values and leadership capabilities.
Once designated, FA40 officers attend the Space Operations Officer Qualification Course that includes the National Security Space Institute, the Space 200 course, and seven weeks of Army-focused space training provided by the SMDC Directorate of Training and Doctrine.
“These courses, 11 weeks in total, are the foundation for FA40 education,” said Robert C. Hoffman, chief of U.S. Army Space and Missile Defense School Space Training Division. “This is the course that takes Army officers from their basic branch and teaches them the fundamentals or the ‘science’ of Space Operations.”
Higher-level courses and seminars are also required as the officer progresses,and officers can also attend other training based on the specific requirements of the billet they are being assigned against. These courses include, but are not limited to, the Special Technical Operations course, Tactical Space Operations Course, Space Control Training, Joint Tactical Ground Station or Advanced Space Operations School courses.
While FA40 officers originally comprised the space cadre, the program expanded in 2007 to include other military occupational specialties and areas of concentration, as well as Department of the Army Civilians who perform duties in one of the five space mission categories. There are currently more than 5,000 personnel identified as members of the Army space cadre in all three components throughout the Army.
Connolly emphasized the importance of the growing Army space cadre. “Our Army has an unrelenting dependence on space capabilities to execute unified land operations in support of the combatant commander’s objectives,” he said. “The Army is one of the largest users of space and is also a provider of space-based capabilities. Accordingly, the Army needs Soldiers and civilians who understand the space mission areas and how space is integrated with other warfighting capabilities.
“The Army space cadre is an untapped resource within organizations; with the space domain being a contested environment, the importance of space-enabled capabilities and the Army space cadre will continue to grow,” Connolly said.
Connolly added that every day, millions of Americans swipe credit cards for everything from bank transactions to gas purchases to renting movies, never realizing that each of those swipes relies on a space-based capability for success.
“In our society, space has become so normalized, that most are no longer paying attention,” he said. “However, as military and civilian leadership are increasingly exposed to the capabilities being provided to our national defense through and from space, the requirement to fully understand and employ offensive and defensive measures will
only expand.
“In the Army, FA40s will serve as the core of a cadre appropriately trained and educated to meet these challenges, but they will not be alone,” Connolly added. “Department of the Army civilians and other Soldiers will share the burden and to ensure success, their development and training must be a priority.”
Story by Jason B. Cutshaw, USASMDC/ARSTRAT Public Affairs
Better Comms for Warfighters Goal of New General Atomics Contract
General Atomics Electromagnetic Systems has been awarded a Department of Defense Ordnance Technology Consortium (DOTC) contract from Advanced Technology International for the Army Resilient Global on-the-move SATCOM (ARGOS).
ARGOS is a satellite system intended to provide Ultra High Frequency (UHF) and Very High Frequency (VHF) Beyond Line of Sight (BLOS) assured communications and Unattended Ground Sensor (UGS) data capture capabilities for use by the United States Army.
Nick Bucci, vice president for Missile Defense and Space Systems at GA-EMS said that their team has demonstrated success in the rapid design, development, test, and launch of satellite systems like ARGOS, and that ARGOS will play an important role in delivering beyond the horizon assured communications for the Army Component and Combatant Commanders. A satellite-based system will provide assured communications for future warfighters whenever and wherever they need it.
The U.S. Army and Combatant Commanders are involved in countering transnational organized crime, humanitarian assistance/disaster relief, peacekeeping operations support, training and exercise, multi-national engagements, and human rights efforts. Not only will ARGOS support the needs of the U.S. Army, but also the Combatant Commanders and Partner Nations.
GA-EMS has successfully flown eleven satellites, providing concept to on-orbit integrated system solutions to support a variety of defense and aerospace applications. GA-EMS specializes in developing space satellite system solutions, including emerging technologies for 3U to 6U CubeSats and small satellites that offer a high degree of configuration and payload flexibility.
www.ga.com/ems
SSL Partners with NASA JPL and University of Michigan for SunRISE
SSL, a business unit of Maxar Technologies (formerly MacDonald, Dettwiler and Associates Ltd.) (NYSE: MAXR; TSX: MAXR), has partnered with a team at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) and the University of Michigan (UM) selected by the agency to conduct a Phase A mission study under NASA’s Explorers Program.
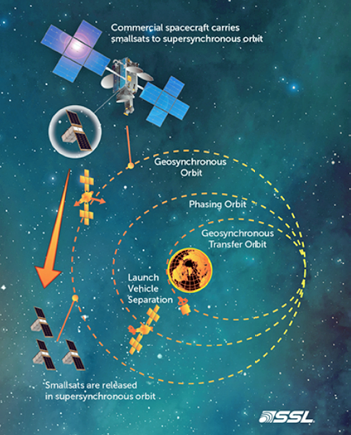
SSL’s role in the mission, called the Sun Radio Interferometer Space Experiment (SunRISE), is to provide a ride beyond geosynchronous orbit (GEO) for a constellation of science-gathering smallsats. SSL will use its Payload Orbital Delivery System (PODS) technology to dispense the small satellites on-orbit as free-flyers.
Mission Principal Investigator Justin Kasper, Associate Professor in the University of Michigan’s Climate and Space Sciences and Engineering Department, will lead the SunRISE team that will use the small satellite constellation, operating as a synthetic aperture radio telescope, to address the critical heliophysics problems of how solar energetic particles are accelerated and released into interplanetary space. Heliophysics is the study of how the Sun affects the environment of the Solar System. By sharing a ride to space on an SSL-built satellite with PODS, the SunRISE mission benefits from the frequency of commercial launch schedules and a significantly reduced launch cost compared to a dedicated mission.
SSL developed PODS in conjunction with the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), with the expectation that it will play a key role in enabling cost-effective, high tempo access to space for small payloads on a wide variety of important commercial, government, and scientific missions beyond LEO.
NASA is also leveraging SSL’s commercial capabilities and experience to help reduce cost on a variety of next-generation missions that enable groundbreaking robotics and automation technologies. These include a NASA Discovery Mission to explore the asteroid Psyche, the Restore-L mission to service satellites in LEO, and the Dragonfly program, which will demonstrate robotic satellite assembly on-orbit.
Richard White, the President of SSL Government Systems, added that the Payload Orbital Delivery System was developed as an innovative solution for smallsats that need to reach GEO and beyond. The PODS system helps to provide flight opportunities for cost-capped missions that wouldn’t otherwise be feasible.
 www.sslmda.com
www.sslmda.com
clasp.engin.umich.edu
Hot-Fire Test for U.S.A.F. by Aerojet Rocketdyne
Another milestone for Aerojet Rocketdyne, as this company’s hot-fire test of a controllable solid rocket motor was successful in demonstrating “the increased capabilities of an advanced, controllable solid rocket motor system.”
This milestone was recently achieved by completing a successful hot-fire test of a controllable solid rocket motor under the U.S. Air Force Demonstration and Validation Post Boost Study A program.
Aerojet Rocketdyne CEO and President Eileen Drake said that this hot-fire test successfully demonstrated the increased capabilities of an advanced, controllable solid rocket motor system, and that applying this technology could provide increased mission flexibility and capability in a future post boost propulsion system.
Post boost propulsion systems are a critical element of strategic and missile defense systems for final payload positioning and deployment.
The Post Boost Study A program was aimed at identifying emerging propulsion concepts using a trade study approach and selecting high potential candidates for demonstration of technical maturity.
Vice President of Defense Advanced Programs Tyler Evans said this program allowed us to evaluate various advanced technology propulsion systems and select one of the most promising — a controllable solid rocket motor system for hardware demonstration testing. He continued that maturing this critical technology now will undoubtedly pay future dividends as the nation looks to modernize its strategic deterrent capabilities in the coming years.
www.aerojetrocketdyne.com


