Successful Launch for SMC + Partners’ Fourth GPS III Satellite
The U.S. Space Force, Space and Missile Systems Center (SMC) and its mission partners successfully launched the fourth Global Positioning Systems (GPS) III satellite at 6:24 p.m. EST, November 5, 2020, from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida.
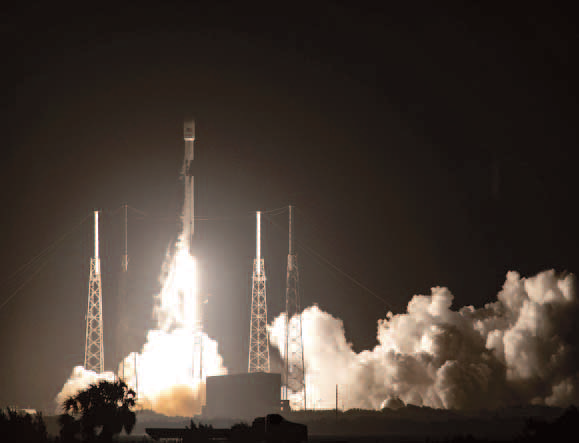

The Lockheed Martin-built satellite was carried to orbit aboard a Space Exploration Technologies Corporation (SpaceX) Falcon 9 launch vehicle.
“The launch of GPS III SV04 is a testament to SMC’s ability to rapidly and safely deliver new capabilities on orbit,” said Cordell DeLaPena, U.S. Air Force program executive officer for SMC’s Space Production Corps.
“I’m proud of my team’s 83rd successful National Security Space Launch and look forward to our future missions with SpaceX,” said Col. Robert Bongiovi, SMC’s Launch Enterprise director. “Ultimately, our ability to embrace innovation with our launch providers advances warfighter’s capabilities while lowering costs to the U.S. Government and its taxpayers.”
GPS III SV04 separated from its upper stage approximately 90 minutes after launch. Engineers and operators at Lockheed Martin’s Waterton Facility will now begin on-orbit checkout and tests, which are estimated to complete in approximately one month. Operational use is expected to begin in a few months.
“The GPS III program continues to make strides in modernizing the GPS constellation for the U. S. Space Force while maintaining the gold standard for position, navigation and timing,” said Col. Edward Byrne, Medium Earth Orbit Space Systems Division chief.
GPS III SV04 will join the current GPS constellation comprised of 31-operational spacecraft. GPS III, the newest generation of GPS satellites, brings new capabilities to users, including three times greater accuracy and up to eight times improved anti-jamming capabilities.
The U.S. Space Force’s Space and Missile Systems Center is located at the Los Angeles Air Force Base in El Segundo, California. SMC’s portfolio includes space launch, global positioning systems, military satellite communications, a defense meteorological satellite control network, range systems, space-based infrared systems and space situational awareness capabilities.
The fourth Lockheed Martin (NYSE: LMT)-built Global Positioning System III (GPS III) satellite is now headed to orbit under its own propulsion. Following a successful launch on November 5, GPS III Space Vehicle 04 (GPS III SV04) separated from its rocket and is now using onboard power to climb to its operational orbit, approximately 12,550 miles above the Earth.
About 89 minutes after a 6:24 p.m. EST liftoff from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Florida, U.S. Space Force (USSF) and Lockheed Martin engineers at the company’s Denver Launch and Checkout Operations Center declared GPS III SV04 “separated” from its SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and “flying” under their control.
In the coming days, GPS III SV04’s onboard liquid apogee engine will continue to propel the satellite toward its operational orbit. Once it arrives, the engineers will send the satellite commands to deploy its solar arrays and antennas and prepare GPS III SV04 for handover to Space Operations Command.

GPS III SV04 is the latest next-generation GPS III satellite Lockheed Martin designed and built to help the U.S. Space Force modernize today’s GPS satellite constellation with new technology and capabilities. GPS III satellites will provide significant capability improvements over previous GPS satellites, including:
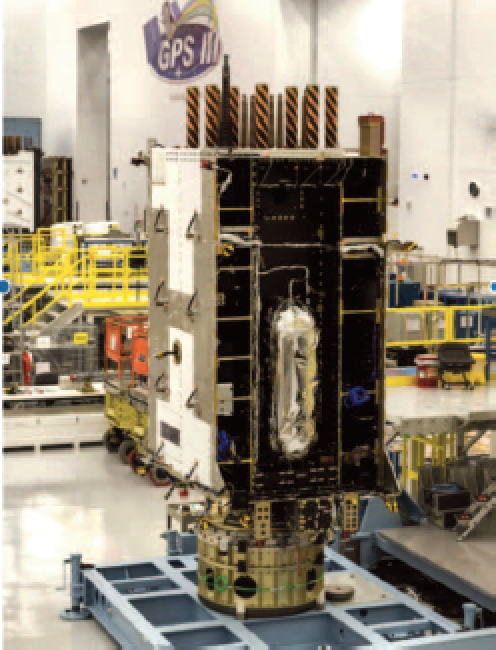
GPS III SV04 photo is courtesy of Lockheed Martin.
• Three times better accuracy
• Up to eight times improved anti-jamming capabilities
• A new L1C civil signal, which is compatible with international global navigation satellite systems, such as Europe’s Galileo, to improve civilian user connectivity
GPS III SV04 will also be the 23rd Military Code (M-Code) signal-enabled GPS space vehicle on orbit, continuing the Space Force’s plan to fully field the more-secure, harder-to-jam and spoof GPS signal for military forces.
GPS is part of the U.S.’s critical national infrastructure, driving an estimated $300 billion in annual economic benefits and responsible for $1.4 trillion since its inception. Globally, more than four billion military, civil and commercial users depend on GPS’ positioning, navigation and timing signals.
“With GPS III we are focused on rapidly fielding the best capabilities to the Space Force’s Positioning, Navigation and Timing (PNT) Mission,” said Tonya Ladwig, Lockheed Martin’s Acting Vice President for Navigation Systems. “We are proud of our industry-government team on the launch of GPS III SV04. GPS III SV05 is already ‘available for launch’ and just waiting to be called up.”
Kratos Debuts OpenSpace™ Platform To Support Software-Defined Ground Systems
Kratos Defense (Nasdaq: KTOS) has released OpenSpace™, a software platform and family of virtual products that enable satellite operators, Ground-as-a-Service (GSaaS) providers and others in the space services supply chain to create fully software-defined, dynamic ground systems.

OpenSpace is a leap forward in ground network technologies that allows operators to apply advances in Software-Defined Networking (SDN) to the special needs of the space industry. SDN technology is already common in the broader communications and IT worlds, however adoption of SDN has been slower in the space industry, in large part because of the unique challenges of virtualizing Radio Frequency (RF) equipment and reliably digitizing the RF waves that are the staple of satellite operations.
Kratos has solved these challenges by virtualizing hardware components in its quantum™ line and by reliably digitizing RF signals for processing in digital environments. Now, with OpenSpace, Kratos moves beyond virtualization to add the orchestration, control and management capabilities that can create truly dynamic ground systems in which practically every element of the network potentially can become software-defined—almost all except the satellite and antenna.
By actively coordinating Virtual Network Functions (VNF) as service chains instead of purpose-built hardware components, operators can enhance the adaptability, resiliency, security and reliability of their ground systems. Ground functions that once took weeks to implement manually are now orchestrated as service chains with OpenSpace, making systems dramatically more responsive to real time changes in network resources, user demand and threats.
According to Kratos, OpenSpace disrupts the decades-long paradigm of ground networks based upon purpose-built, often proprietary hardware and stove-piped software applications in favor of standards-based, fully integrated, end-to-end service delivery running on COTS servers or in the cloud. OpenSpace’s comprehensive SDN framework means operators can leap ahead in the transformation of their ground systems, employing accepted techniques from the broader communications industry.
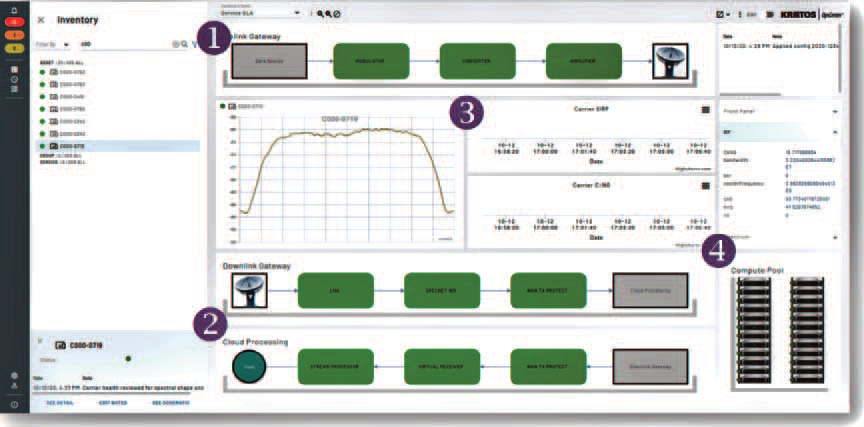
The OpenSpace platform architecture incorporates four operating areas: OpenSpace VNFs are software applications that replace dedicated satellite hardware technology, such as receivers and recorders. Every OpenSpace VNF is built for cloud-native deployment on generic x86 compute resources without the need for Field Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGA) or Graphics Processing Units (GPU). OpenSpace VNFs can be purchased standalone or together as service chains.
The OpenSpace Controller is the brain center that coordinates the deployment of VNFs as service chains to support a specific Service Level Agreement (SLA) or mission. Using industry-standard interfaces such as MEF LSO, the OpenSpace Controller can orchestrate OpenSpace and third-party VNFs and interface directly with third-party service and resource orchestration frameworks, enabling truly dynamic network operation and vendor-independence.
OpenSpace OpsCenter™ is OpenSpace’s unified manager which administers the service chain life cycle and bridges management functions across legacy analog components. Today, OpsCenter manages both physical and virtual network components and will soon add carrier management and ultimately satellite Command & Control (C2), all within a common API set, user interface and data model.
OpenSpace Digitizers reliably convert RF signals at any frequency band into a VITA49 Digital IF format that can be easily transported globally over a standard Ethernet/IP network. It preserves both frequency and timing characteristics, even over impaired Ethernet/IP network links when working with OpenSpace’s VNF for WAN Transport Protection.
OpenSpace removes that bottleneck, bringing ground systems to par with their surrounding technologies and advancing the movement to disaggregate space systems from ground systems. Numerous, high-value advantages result, including: Virtual functions can run on generic, inexpensive computers or in the cloud instead of expensive, purpose-built equipment. Intelligence can be built into the network to implement new services quickly, shifting resources to where they are needed; a process that can take weeks in today’s static ground systems.
Ground systems can potentially support not just satellites from multiple manufacturers, but multiple orbits simultaneously. The network achieves far greater levels of security, self-healing and resiliency to changing conditions such as hacking or interference. It becomes possible to bridge the data, transport and management aspects of satellite systems to provide a unified interface that describes service chains across network components, enables automation of those service chains, and delivers a common operating picture across all resources.
For more information about the OpenSpace platform and the products introduced in the OpenSpace family, visit this direct infolink…
In addition to the release of the OpenSpace Controller, Kratos separately announced two new VNFs for EO and Sensing service chains, the OpenSpace WAN Transport Protector (OWTP) and the OpenSpace Stream Processor/Recorder (OSPR). Kratos debuted its first VNF, the OpenSpace Wideband Receiver, in August of this year.

Yves Pitsch
According to Yves Pitsch, Principal Product Manager, Azure Networking at Microsoft of Microsoft’s recently announced Azure Orbital Ground Station-as-a-Service offering, which employs OpenSpace products in its service architecture. “An SDN-based architecture like OpenSpace’s is critical to our ability to provide our customers with a platform that is complete, economical and easy to use. Virtualized operations provide us with the flexibility and scalability we need to optimally support many different customers, missions, satellites and other specialized needs without specialized hardware.”

Phil Carrai
“Going back to the very early days of space missions, satellites and their ground systems were designed from scratch to work together in tandem using custom hardware and software,” explained Phil Carrai, President of Kratos’ Space, Training & Cybersecurity division. “Over time, those ties have loosened as both satellite and network technologies have evolved—in fact, for decades Kratos has been a leader in developing standards-based signal processing and ground management products that work with multiple satellites in multiple mission frameworks—however the ground and the satellite have not been able to operate fully independently until now with OpenSpace.”

Greg Quiggle
Communications networks in other industries have increasingly adopted virtualization and, more recently, SDN as their new paradigm. Where virtualization converts functions that once were hardware into software, an SDN-based model like OpenSpace goes much further by adding a standards-based platform logic coordinating these virtual components. “SDN technology makes communications and IT networks faster and more automated, resilient and flexible so that they can change and adapt rapidly to changes in network supply, demand and threats,” commented Greg Quiggle, VP of Product Management for Kratos Space. “Ground systems must keep pace with these innovations. Otherwise, today’s purpose-built, hardware-intensive ground systems will increasingly be the static bottleneck between two dynamic, software-defined endpoints.”
iDirect Government’s Evolution® Platform Receives IA + Cybersecurity Enhancements
iDirect Government (iDirectGov) has enhanced their Evolution® platform with information assurance (IA) and cybersecurity, all as a part of a multi-layered approach to security.

Two main technology advancements in Evolution 4.2.2.0 include SHIELD, a security service for remotes, and Communication Signal Interference Removal (CSIR™), a real-time streaming technology to mitigate interference. These enhancements are fully integrated across iDirectGov’s 9-Series satellite modems.
To address vulnerabilities in satellite modems, SHIELD provides periodic IA security updates for the 9-Series modems. These remote-side packages are created using the same capability that the Defense Information Systems Agency‘s (DISA’s) Assured Compliance Assessment Solution (ACAS) recognizes. When installed, SHIELD addresses vulnerabilities based on the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) and Nessus ID database on the satellite modem and delivers IA posture across the SATCOM network.
CSIR excision technology effectively mitigates a wide range of interferers, from carrier waves to multiple strong interferers, without requiring any prior information on them. CSIR can locate fast-moving and intermittent interference and restore the quality of the original signal, without requiring additional hardware. This helps to combat adversaries who are increasing their implementation of signal intelligence (SIGNET) to attack military and government spectrum use by jamming transmissions intended for radio communications, radar and various operations.
SHIELD and CSIR add to the Evolution platform’s award-winning, high standard of transmission security (TRANSEC) to create a multi-layered highly secure solution. Other enhancements as part of this approach include dual-mode and beam choice features to mitigate threats to a SATCOM network. Dual-mode enables the 9-Series modems to operate on both government-owned and commercial networks, giving the user both flexibility and ubiquitous coverage. Beam choice allows operators to manually select the ideal beam for their missions rather than using the automated process.

John Ratigan
“Our customers are becoming more proactive and are seeking ways to reinforce defenses before problems occur, and we are moving forward with our customers to secure our solutions with our specialized product enhancements,” said John Ratigan, President of iDirectGov. “Safeguarding critical communications signals is important, and any satellite modem attempting to operate in a congested environment, especially where adversaries may be intentionally jamming signals, can benefit from CSIR.
Ratigan continued, “Whether attacks are intentional or unintentional, the CSIR interference mitigation is a core feature of the Evolution system to ensure holistic communication integrity and availability. Implementing a Defense-in-Depth approach allows defense, homeland security, first responders and other government users to have reliable and secure communications to support their critical missions. iDirectGov’s approach to SATCOM cybersecurity provides the means to plan, detect, locate, remove, report and deploy mitigation to signal interference.”
L3Harris Receives Manpack Radio Award From U.S. Special Operations Command
U.S. Special Operations Command (USSOCOM) has awarded L3Harris Technologies (NYSE:LHX) an initial $82 million, full-rate production order for the company’s new Falcon IV® AN/PRC-167 multi-channel manpack radio that will provide Special Operations Forces (SOF) with advanced communications capabilities.
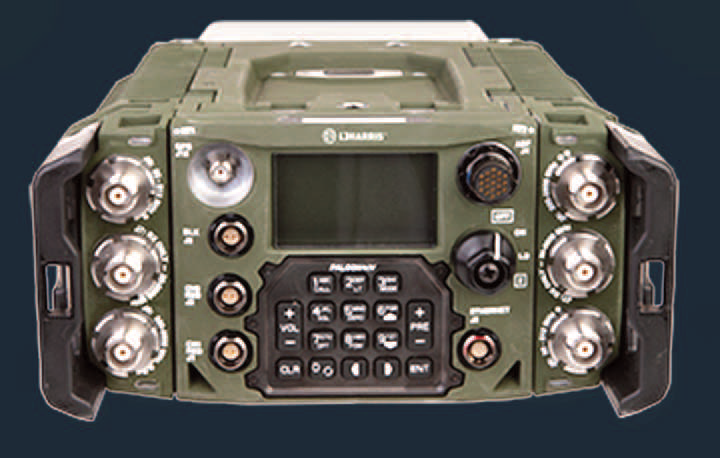

The order is part of a $255 million IDIQ contract awarded by USSOCOM under the Next Generation Tactical Communications (NGTC) program to deliver multi-channel manpack radios. Prior to the award of the NGTC multi-channel manpack contract, USSOCOM also awarded the company an IDIQ contract for Falcon IV® AN/PRC-163 multi-channel handheld radios.
These multi-channel manpack and handheld radios are key elements of USSOCOM’s next generation tactical communications. They provide complete DoD and coalition interoperability with the disruptive technology needed to enable mission success against current and future threats.
The AN/PRC-167 harnesses the power of multiple tactical devices converged into a single manpack radio. This compact, lightweight manpack delivers USSOCOM’s tactical mission network and ensures interoperable connectivity with partner forces.
The AN/PRC-167 is engineered to meet multi-domain challenges of dismounted, vehicular, maritime, and airborne missions. It simultaneously runs a broad portfolio of line of sight, networking, SATCOM and resilient waveforms on each of the two 30-2600 MHz primary channels.
Multiple robust mobile ad hoc networking (MANET) waveforms empower Hyper Enabled Operators with information and data analytics at the tactical edge. The software-defined manpack supports fast, in-field software updates to add resilient waveforms and new capabilities.

Dana Mehnert
The L3Harris Mission Module port allows plug-and-play add-on modules to function as a simultaneous third channel. These three channels can operate independently or be crossbanded to exchange voice and data between different radio networks. The initial mission module includes a Full Motion Video ISR receiver, and subsequent modules will add other emerging technologies.
“SOF are constantly pushing boundaries to execute their missions with greater stealth and speed,” said Dana Mehnert, President, Communication Systems, L3Harris. “The AN/PRC-167 provides situational understanding between the tactical edge and command elements, allowing cognitive overmatch in any operational scenario.”


