In Norse mythology, two ravens served Odin, the God of War. They flew out daily to collect information and update Odin on global sightings of enemies and other relevant activities. Their insight provided context, awareness and foresight that enabled Odin to make effective decisions.

Like the ravens, our military and commercial space operations rely on information collectors. RF sensors, radar and Earth Observation (EO) collect data for situational awareness and better decision-making.
Unlike the ravens, who only served Odin, today’s intelligence supports many interests, as global data and services related to space are critically important for strategic military reasons, as well as growing commercial dependence.
Real-time Insight To Work Through Threats
In March of 2023, the public and private Space Information Sharing and Analysis Center (Space ISAC) announced the opening of a new operational Watch Center that focuses on detecting and sharing cyber threat information, as well as real-time insights on various other threats to satellite systems.
Partnering with more than 30 government agencies and a member base of 64 organizations worldwide, the Watch Center will receive real-time data from member companies, such as Kratos.
Erin Miller, Executive Director of the Space ISAC, said, “By sharing information on disruptions to space systems through the Watch Center, we are creating a unified front against potential threats.”
Correlated Space + Terrestrial Data
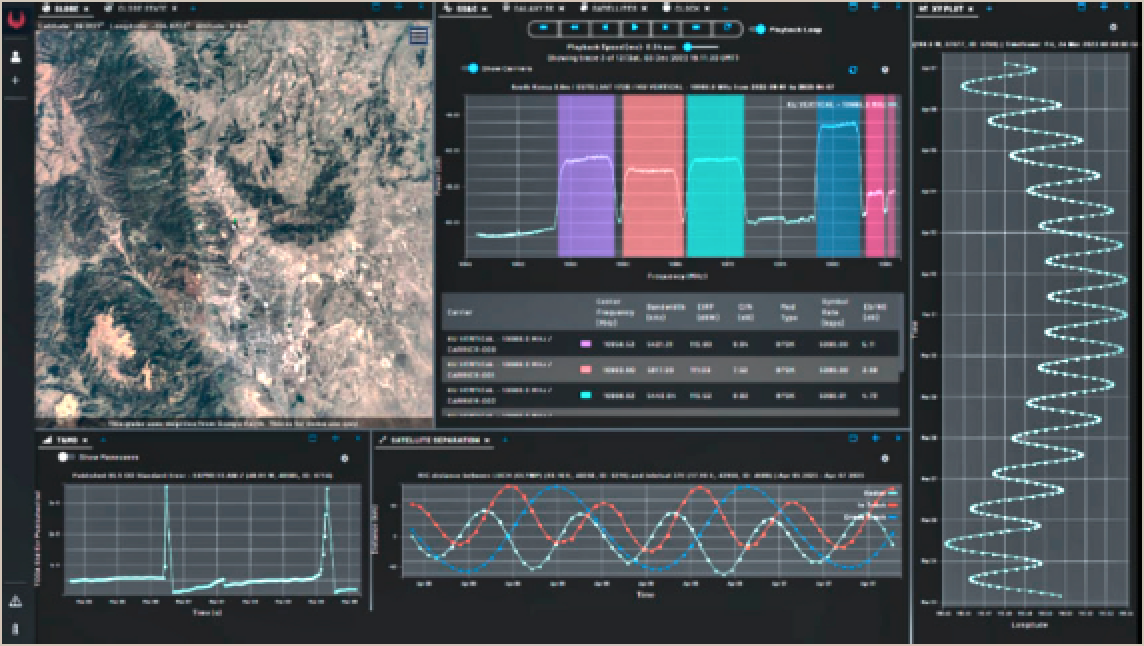
Kratos’ contributions to the Watch Center include access to RF Space Domain Awareness (SDA) data from the Kratos Global Sensor Network (KGSN), a global deployment of more than 140 RF sensors capable of pinpointing satellite locations within 100 meters.
Users access the network through a cloud-based Common Operating Picture (COP) showing data from both space and terrestrial assets. The RF COP is just one of the tools helping the Watch Center improve visibility of attacks on space-based assets. Examples of insights available within the Kratos’ RF COP include:
• Precision ephemeris for space traffic management and orbital slot verification
• Multi-transponder spectrum monitoring and signal characterization
• Detection and characterization of EMI and jamming
• Satellite maneuver detection and real-time alerting
• Rendezvous and proximity operations monitoring
Geolocation Of Terrestrial Transmitters
Frank Backes, Senior Vice President of Kratos Space, said, “We are seeing much more aggressive activity. Adversarial nations have launched satellites that can get close enough to listen in on signals other satellites are sending, and in some cases, threaten those satellites. For private companies to face that threat alone is a big task.”

The Watch Center represents the global space community’s efforts to assist companies with a collaborative environment of commercial and government experts.
Kratos RF COP Reveals RF Data in Real-time
RF Data Fills the Gap
Kratos’ RF SDA services augment today’s traditional resources with tools for understanding and responding to emerging on- orbit threats for military and commercial entities.
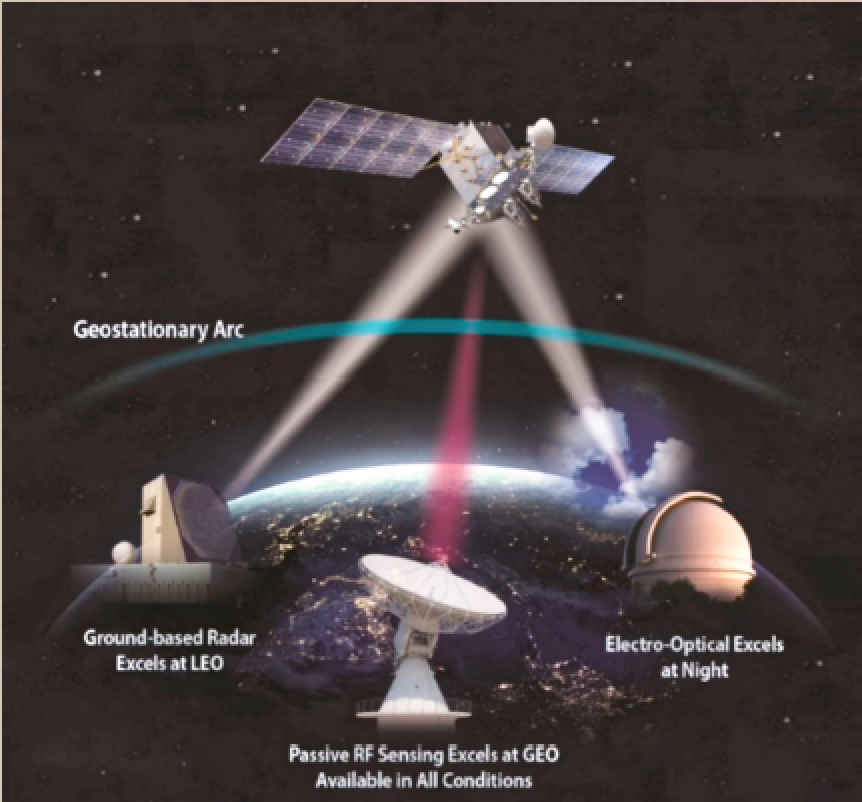
RF-based SDA is unique in that it fills key gaps in traditional SDA systems such as radar and electro-optical. By capturing native radio frequency signals, objects in space can be located, identified, characterized and tracked to analyze satellite missions and operations, and provide response capability to threats and challenges in space.
SDA has become vital to mission success given the increase in commercial space activity and the escalating number of international actors influencing the dynamic theater.
While electro-optical sensors continue to improve in performance, they are still subject to solar exclusion windows during which satellites cannot be observed. Spacecraft operators know this and schedule operations to capitalize on it. In addition to solar exclusions, cloud coverage blinds electro-optical telescopes, while passive RF sensors operate 24/7 in all weather.
To be clear, passive RF sensing complements SDA — it does not replace other sensors. RF sensors can only observe objects that are transmitting, so it’s useful for active spacecraft but are blind to space debris.
Commercial + Military Interests
Analysts at Kratos have been using RF SDA to closely track the Russian spy satellite, Luch Olymp (www.kratosdefense.com/ constellations/articles/espionage-in-orbit-satellite-or-spy). The satellite, ostensibly part of a civilian data relay constellation, exhibits unusual behavior leading experts to conclude its mission is signals intelligence.
RF observations confirm Luch Olymp transits the GEO belt, frequently stopping near military and commercial satellites, presumably capturing their communications.
After a 63,000 km relocation in August of 2022, it is holding a steady longitude of 18 degrees West, a slot co-located with Intelsat 37E. This extended stay represents one of Luch Olymp’s longest periods without relocation.
The ongoing conflict in Ukraine may influence this satellite positioning. Luch Olymp’s current orbital slot supports trans-Atlantic traffic from Europe, North America and Africa, hosting a variety of users that may be of interest to the Russian government.
Based on observed offensive actions in the space domain since February 2022, this longitude appears to support Russian strategic operations in Ukraine.
At the grand opening of the Watch Center, Commander of U.S. Space Operations Command, Lt. Gen Whiting, said, “By monitoring both space and terrestrial activities, we can defend collectively against adversaries and reduce response times from months to minutes — an unprecedented achievement.”

Kratos owns and operates the world’s most precise global commercial ground network of RF
sensors. Strategically positioned apertures around the globe enable precise and persistent RF sensing, providing insight for missions in defense, intelligence and commercial operations. The global network covers L-, S-, C-, X- and Ku-bands. Kratos’ state-of-the-art OpenSpace® Platform manages and controls the status of the global network.
Whiting reemphasized the importance of coordinated cyberthreat sharing at the recent Space Symposium, saying that the Watch Center will help ensure information is not siloed among commercial and military operators.
Space Force leaders have publicly acknowledged that cybersecurity is the soft underbelly of global space networks, which was exposed in the 2022 cyberattack on a commercial SATCOM provider.
As space becomes an increasingly contested domain, the Watch Center is enabling military and commercial operators to share threat intelligence to better detect, deter and withstand adversarial cyberattacks.
Global Interests, Common Goal
Effective intelligence to understand the global space and cyber operating environment depends on having the right information, at the right time.
The ravens provided situational data to Odin, enabling him to have greater understanding about his adversaries and his world in general. In our real world, intelligence must accommodate more than one global interest. Having platforms such as the Space ISAC Watch Center, that can share situational awareness data with multiple entities with common global interests, is essential to defending our space assets.

Author Michael Clonts is the Director of Space Domain Initiatives at Kratos. He shares experience from a 20-year career in satellite communications, signal monitoring, software engineering, and product management.
Please visit this direct link for more information on Kratos SDA services.
For more information about Luch Olymp, visit Kratos Constellations and read “Espionage in Orbit: Satellite or Spy?”


