Eutelsat Garners An Equity Stake In OneWeb
Eutelsat Communications (Euronext Paris: ETL) has entered into an agreement with OneWeb for the subscription of a c.24% equity stake, becoming a leading shareholder of the company alongside the UK Government and Bharti Global — Eutelsat will invest $550 million in OneWeb, with closing expected in H2 2021 subject to regulatory authorizations.

With much of its global network already deployed, the OneWeb constellation will operate 648 satellites in LEO offering low latency. This first generation of satellites will offer significant regional coverage by the end of 2021, reaching global coverage the following year.
OneWeb will be the first complete, non-geostationary constellation with truly global coverage, significantly ahead of competing projects. It will deliver 1.1 Tbps of capacity addressing the government, fixed data and mobility markets.
Plans include a second-generation constellation that will provide significant enhancements in terms of capacity, flexibility and economics. It anticipates annual revenues of circa $1 billion within three to five years following the full deployment of the constellation, with a partnership approach and profitable wholesale business model.
Eutelsat’s investment leaves OneWeb almost fully funded and the company is well advanced in terms of securing its remaining funding needs this year. Eutelsat’s investment will come with similar governance rights to the UK Government and Bharti, including board representation, where its position and expertise as one of the world’s leading satellite operators will help to drive the success of the new constellation.
The investment will be 100% cash financed through Eutelsat’s liquidity position of 1.9 billion euros as at end- March 20211 and the $507 million US C-Band auction proceeds, and will be accounted for under the equity method. It is consistent with Eutelsat’s financial hurdle rates and does not alter its financial objectives, which are fully confirmed, including the medium-term net debt / EBITDA target of c.3x and a commitment to solicited Investment Grade credit ratings. Eutelsat’s policy of a stable to progressive dividend is also reiterated.
Commenting on the agreement, Rodolphe Belmer, Eutelsat’s Chief Executive Officer, said, “We are excited to become a shareholder and partner in OneWeb in the run up to its commercial launch and to participate in the substantial opportunity represented by the non-geostationary segment within our industry. We are confident in OneWeb’s right to win thanks to its earliness to market, priority spectrum rights and evolving, scalable technology. We look forward to working alongside the UK Government, Bharti and the other shareholders to open new opportunities and market access to ensure OneWeb maximizes its potential. OneWeb will become our main growth engine outside our broadcast and broadband applications, as we continue to maximize cash-flow extraction from our highly profitable heritage business and grow our fixed broadband vertical leveraging our geostationary assets.”

OneWeb Executive Chairman, Sunil Bharti Mittal, said, “We are delighted to welcome Eutelsat into OneWeb family. As an open multi-national business, we are committed to serving the global needs of Governments, Businesses and Communities across the Globe. Together we are stronger, benefiting from the entrepreneurial energy of Bharti, extensive global outreach of UK and long-term expertise of the satellite industry at Eutelsat. OneWeb, with its innovatory approach, is poised to take a leading position in LEO broadband connectivity.”
Neil Masterson, Chief Executive Officer of OneWeb added, “As OneWeb accelerates the deployment of its fleet and engages in discussions with potential customers, we welcome the powerful support of Eutelsat during the next exciting phase of our journey together, benefiting both companies equally. Eutelsat is a great partner for OneWeb thanks to our high level of complementarity in terms of technology, assets, addressable markets, geographic reach and institutional relationships.”
1€1.4 billion when restated for the upcoming € 500 millionbond maturity
ULA Powers NROL-82 To Orbit
A United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket lifts the NROL-82 mission from Vandenberg AFB in California. This is the 143rd mission for United Launch Alliance and the company’s 90th mission in support of U.S. national security and the 31st for the U.S. National Reconnaissance Office (NRO). This is the 386th Delta launch since 1960, the 13th Delta IV Heavy and the 9th Heavy for the NRO. NROL-82 is also the NRO’s first launch from Vandenberg since January of 2019.

United Launch Alliance’s Delta IV Heavy is a heavy-lift launch vehicle, the largest type of the Delta IV family and one of the world’s most powerful rockets.
The Delta IV Heavy configuration is comprised of a common booster core (CBC), a cryogenic upper stage and a 5-meter-diameter payload fairing (PLF). The Delta IV Heavy employs two additional CBCs as liquid rocket boosters to augment the first-stage CBC. The Delta IV Heavy can lift 28,370 kg (62,540 lbs) to LEO and 14,210 kg (31,330 lbs) to GEO. This is an all liquid-fueled rocket, consisting of an upper stage, one main booster and two strap-on boosters.
The NRO’s next launch is NROL-11, scheduled for later this quarter from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility, Virginia.
Engines supplied by Aerojet Rocketdyne provided the lifting power for the successful launch of a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta IV Heavy rocket carrying a classified U.S. National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) NROL-82 payload.
The Delta IV Heavy features three core stages in a side- by-side configuration, each powered by a single Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-68A engine generating 705,000 pounds of thrust at liftoff. The RS-68A, developed specifically for the Delta IV, is the world’s most powerful hydrogen- fueled engine. The vehicle’s second stage is powered by a single RL10B-2, hydrogen-fueled engine generating 24,750 pounds of thrust. The Delta IV Heavy’s propulsion systems also feature pressurant tanks built by Aerojet Rocketdyne’s ARDÉ subsidiary.
Eileen P. Drake, Aerojet Rocketdyne CEO and president, said, “Our reliable, flight-proven RS-68 and RL10 engines have supported ULA’s Delta IV Heavy missions since the rocket’s first flight in 2004 and have continued with 100% mission success for nearly two decades.”
“The payload launched today is one of the most complex payloads our nation launches and it provides vital space capability,” said Col. Robert Bongiovi, director of SMC’s Launch Enterprise. “That’s why we have to get it right the first time. The launch team performed flawlessly and I am so proud of the work they do to ensure 100 percent mission success.”
ULA’s next launch is the Space Based Infrared System (SBIRS) GEO Flight 5 mission for the U.S. Space Force from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida.
Northrop Grumman Corporation (NYSE: NOC) supported the successful launch of NROL-82) — the company’s contributions to the ULA Delta IV heavy rocket include 11 key large composite structures including three thermal shields that house and protect the engines during flight; three centerbody structures that connect the liquid oxygen (LOX) and liquid hydrogen (LH2) tanks; the payload fairing that provides protection to the payload; the composite interstage on the center common booster
core; the nose cones on the two strap-on boosters and one set of X-panel structures that connect the upper stage LOX tank with the upper stage hydrogen tank. The large-scale composite structures measure four to five meters in diameter and range from one to 15 meters in length. Northrop Grumman produced them all using advanced hand layup, machining and inspection techniques at the company’s manufacturing facility in Iuka, Mississippi.
Other Northrop Grumman products integrated on the ULA Delta IV heavy launch vehicle include four booster separation rocket motors for the launch vehicle manufactured at Northrop Grumman’s Rocket City, West Virginia facility. The motors ignite when the two side- mounted common core stage burns are complete to assist booster separation from the center core.
Northrop Grumman also designed and produced the nozzles for the three Aerojet-Rocketdyne RS-68 engines, as well as the nozzles’ innovative thermal protection material, and the propellant tank for the Delta IV upper stage roll control system at its Commerce, California facility. and the propellant tank for the Delta IV upper stag control system at its Commerce, California facility.
USSF / SMC Awards Raytheon Intelligence & Space GPS OCX 3F Contract
The United States Space Force’s Space and Missile Systems Center (SMC) awarded a $228 million contract to Raytheon Intelligence and Space for the Global Positioning System (GPS) Next Generation Operational Control System (OCX) Follow-On (OCX 3F) on April 30.

The OCX 3F program is part of the GPS Enterprise Modernization effort. GPS is a satellite-based radio navigation system that provides accurate positioning, navigation, and timing (PNT) for military and civil users worldwide.
The GPS OCX Blocks 1 & 2 System, planned for delivery in 2022, will represent a major evolution in capabilities for the GPS enterprise. In addition to supporting the latest DoD standards and practices for cybersecurity, it also supports a number of advanced features over the legacy GPS Ground Segment.
These new features include an enhanced and expanded monitor station network for improved cybersecurity and improved anti-jam capability, enhanced operational capability to control the modernized military signals, support of GPS III boosted earth coverage Military code (M-code), and the monitoring of new Galileo-compatible and safety of life signals.
OCX 3F upgrades the OCX Blocks 1 & 2 system to use the enhanced capabilities of the new GPS IIIF space vehicles being developed by Lockheed Martin..

The OCX 3F program, in combination with the GPS IIIF space vehicle program, ensures PNT will continue to be available for future generations. Raytheon Intelligence and Space will perform the work in Aurora, Colorado, and delivery is expected in July 2025.
“OCX is an adaptive architecture designed to evolve to combat emerging threats. OCX 3F is a great example of modifying the OCX Blocks 1 and 2 software baseline to launch and incorporate the GPS IIIF enhanced satellite capabilities. I look forward to continuing our relationship with Raytheon in delivering the United States Space Force GPS capabilities,” said Barbara Baker, SMC Production Corps Command and Control Systems Division’s senior materiel leader.
“The OCX 3F program office is looking forward to working with Raytheon on this new GPS ground control program. We are ready to take on any challenges and to work full bore to deliver the critical regional high-powered signals and GPS IIIF launch and control capabilities in support of joint warfighters,” said Lt. Col. Grant Spear, SMC OCX 3F materiel leader.

Lockheed Martin Names New Senior Vice President of Government Affairs
Lockheed Martin (NYSE: LMT) has named Christian Marrone as the senior vice president of government affairs, succeeding Robert Rangel, who will retire later this year. Marrone, a current Lockheed Martin vice president of government affairs, has played an active role in many of the most critical issues facing the company. Prior to joining Lockheed Martin in 2019, he successfully served as a senior presidential appointee in both the Bush and Obama administrations in addition to his experience in state and local government and the private sector.
Space Flight Laboratory’s NorSat-3 Maritime Smallsat Launched — Commissioning Underway For The Norwegian Space Agency
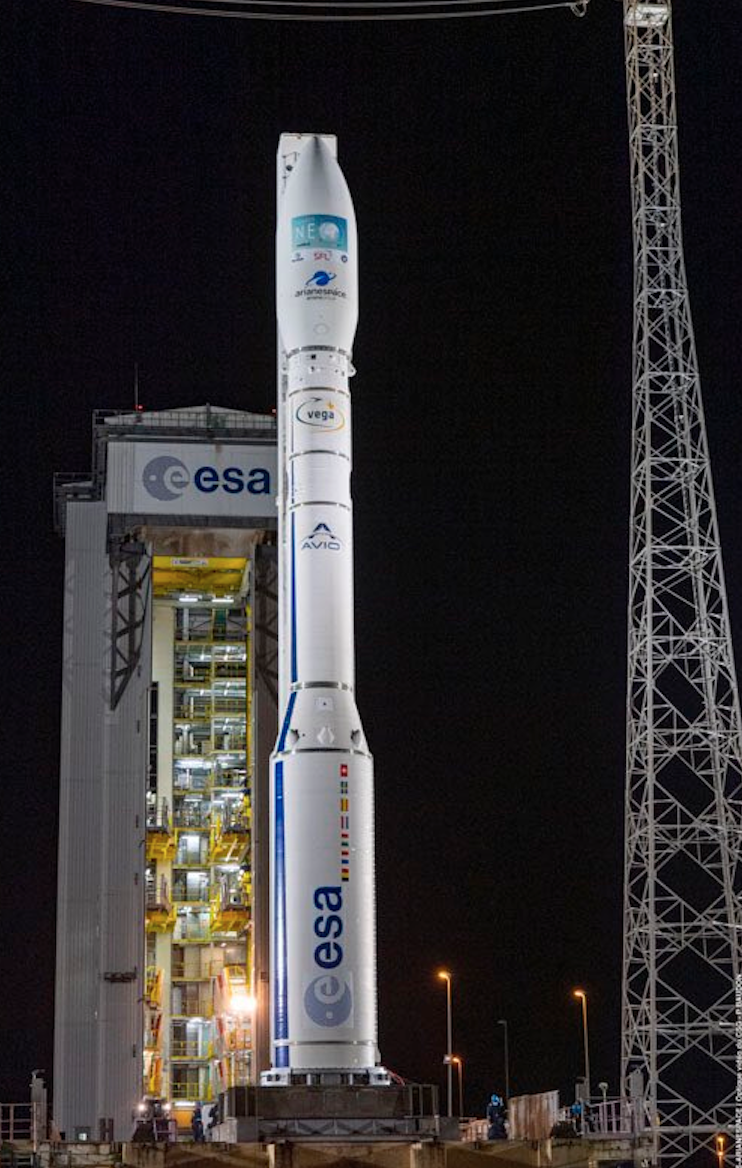

The Norwegian Space Agency has announced the successful launch of the NorSat-3 maritime tracking smallsat, built by Space Flight Laboratory (SFL) in Toronto, successfully launched on April 28, 2012, aboard Arianespace‘s Vega Flight VV18 from the Guiana Space Center in French Guiana — this is the 17th SFL satellite launched within the past eight months.
NorSat-3 carries two instrument payloads. The primary device is an Automatic Identification System (AIS) receiver that acquires messages from civilian maritime vessels to provide information on ship locations and marine traffic.
The smallsat is also equipped with an experimental navigation radar detector developed by the Norwegian Defence Research Establishment (FFI) to augment the AIS receiver.

Combining a navigation radar detector and AIS receiver will potentially provide much better maritime awareness for the Norwegian Coastal Administration, Armed Forces and other maritime authorities.
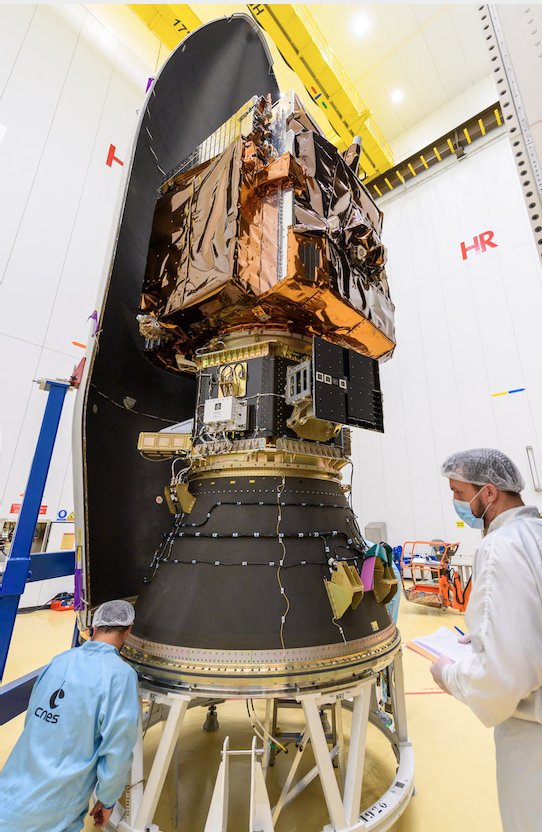

Detection of navigation radar from ships will provide the ability to verify the accuracy of received AIS messages and to detect vessels whose AIS messages have not been received.
SFL developed the 16.5 kg NorSat-3 smallsat on the company’s space-proven, Next Generation, Earth Monitoring and Observation (NEMO) platform, under contract to the Norwegian Space Agency, with funding from the Norwegian Coastal Administration.
SFL also built the NorSat-1 and -2 maritime tracking smallsats now on-orbit and the firm is currently developing the NorSat-TD (Technology Demonstrator) satellite that is slated for launch in 2022.
SFL congratulates Norway on its leadership in spacebased maritime traffic monitoring,” said SFL Director Dr. Robert E. Zee. “NorSat-3 was contacted shortly after launch and is healthy. Commissioning is underway.”
Virgin Orbit Selected By Brazilian Space Agency + Air Force For Orbital Launches
The Brazilian Space Agency (Agência Espacial Brasileira; AEB) and Brazilian Air Force (Força Aérea Brasileira, FAB) announced that Virgin Orbit has been selected to bring orbital launch capability to Brazil, a country which has never successfully completed a domestic launch to orbit.

Thanks to the unique mobility and small footprint of Virgin Orbit’s air-launched system architecture, launches to a wide range of orbital inclinations could quickly become possible without the need for new permanent infrastructure, nor the expansion of existing facilities.
Launches would occur from the Alcântara Launch Center (Centro de Lançamento de Alcântara, CLA) on Brazil’s northern coast, located just two degrees south of the equator. Virgin Orbit’s LauncherOne system, which uses a customized 747 aircraft as its flying launch pad and fully reusable first stage, could conduct launches from the existing airbase at the site, flying hundreds of miles before releasing the rocket directly above the equator or at other locations optimized for each individual mission. The approach enables Alcântara to become one of the only continental spaceports in the world capable of reaching any orbital inclination.
Since construction of the facility began in 1982, Alcântara has hosted dozens of launches of uncrewed, suborbital sounding rockets — but the facility has not yet been used to reach orbit.
By bringing that long-sought capability to Alcântara, Virgin Orbit, AEB, and FAB will create an important new capability for the region while delivering on the promised economic value of the site for the local quilombo communities.
All of the equipment required for Virgin Orbit to conduct a launch to orbit is fully transportable, from the ground vehicles that prepare the rocket for flight to the rocket and aircraft itself — meaning that the team can securely transport the entire system in, conduct a launch campaign, and return to one of the company’s other facilities without requiring any further construction beyond the airbase.
LauncherOne’s first flight from the facility would transform Alcântara into the second orbital-class spaceport in all of South America, and only the fifth in the entire Southern Hemisphere.
Since the start of his term, the President of AEB, Carlos Moura, has stated that making the Alcântara Launch Center a reference for space activities in Brazil and in the world is at the center of the priorities of the Brazilian space program. “Alcântara is one of the most ideal places in the world for launching rockets. It is close to the equator, which increases the launcher’s payload capacity, and allows a wide range of azimuths for launches, with access to all orbits. When we put the Center into operation, we will overcome a historic challenge for the program, which means a commitment to Brazil and the world community towards ever greater achievements for humanity.”

“The people of Brazil have been patiently and diligently working towards orbital launch for many years now, and it will be a tremendous honor to help make that vision a domestic reality,” said Dan Hart, the CEO of Virgin Orbit. “Space launch will bring a key capability to the nation and to the space community, while helping address the long-standing needs of the local community. There’s really no better place on the planet than Alcântara for an equatorial launch site. And with hundreds of miles of cross range on our flying launch pad, the potential is boundless. We’re eager to work with our colleagues at AEB and FAB to bring this vital new capability to Alcântara.”
SpaceLink + Mynaric Join Forces For Satellite Relay Network Laser Comms Development

Mynaric and SpaceLink have agreed on the framework of a partnership to expand Mynaric’s laser communication product portfolio for use in SpaceLink’s data relay network. The strategic relationship will help drive forward the SpaceLink satellite relay service, which provides secure, continuous, high-capacity communications between LEO spacecraft and the ground.
The companies will work together to expand Mynaric’s product portfolio with an optical inter-satellite link (OISL) terminal for satellites in MEO, where the SpaceLink constellation will operate. The new terminal will also be compatible with the Space Development Agency (SDA) Transport Layer.
Mynaric will supply more than 40 OISL terminals as part of the plan outlined in a term sheet that includes units of the new, advanced product for satellites in MEO as well as units of Mynaric’s CONDOR terminals for SpaceLink LEO customers. SpaceLink and Mynaric have also agreed to an option that would increase the number of terminals delivered upon SpaceLink’s expansion of its MEO constellation.
Laser communication technology is critical for SpaceLink to build the communications superhighway for the new space economy. Mynaric’s product portfolio is a natural choice as it meets SpaceLink’s programmatic requirements, provides high performance, and is fully compliant with the OISL Standard driven by the SDA. This is a major benefit that allows SpaceLink to serve the largest possible range of commercial and government customers.
SpaceLink is building its high-capacity data relay network to meet pent-up demand for continuous, fast, and secure access to the growing amount of data available from space. The Always in Sight™ constellation helps satellite operators maximize the value of on-orbit assets with near real time transmission of user data to the ground for immediate access via the Internet, private cloud, or other secure delivery. Mynaric was selected as a supplier to support SpaceLink’s mission given its industrialized approach toward the production of advanced laser communication products. its industrialized approach toward the pro advanced laser communication products.

Pictured, left to right: SpaceLink’s Rob Singh, CTO, Larry Rubin, COO, Dave Bettinger, CEO. Mynaric’s Tina Ghataore, CCO, Joachim Horwath, CTO, Bulent Altan, CEO, Ali Younis, VP U.S. Business Development



