SSC launces 6 satellites for MDA + SDA on SpaceX Falcon 9
Space Systems Command (SSC) and its mission partners successfully launched the U.S. Space Force (USSF)-124 mission on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket today at 5:30 p.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 40, Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, Florida.
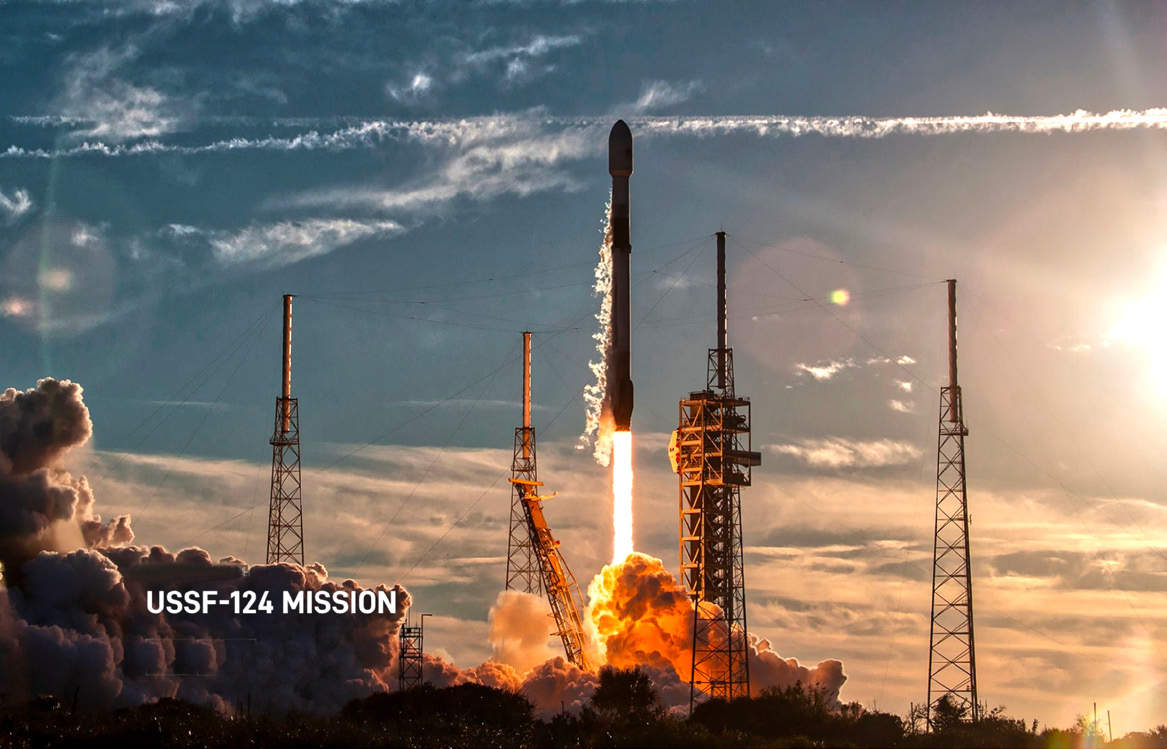

The satellites for the Missile Defense Agency (MDA) and Space Development Agency (SDA) were safely delivered to their intended orbit.
USSF-124’s mission was to place a new generation of missile detection, missile tracking and networked communications satellites into orbit, bringing new capabilities to the nation and its Allies.
This was the first NSSL mission of 2024 to use a flight-proven Falcon 9 booster that previously supported six earlier missions.
The rapid reusability of SpaceX’s Falcon 9 benefits all launch customers and the Space Force’s continued partnership with SpaceX provides for manifest flexibility and cost savings.
“We’re proud to support both the MDA and SDA with this co-manifested National Security Space Launch,” said U.S. Space Force Col. Jim Horne, senior materiel leader for SSC’s Launch Execution Delta. “We worked side-by-side with our launch service provider and space vehicle partners to achieve the mission on-time and with precision. Today’s mission supports our global warfighters and people across the globe in every facet of life.”
“We’re reaping the benefits of this innovation with every launch. We began working this concept seven years ago, understanding the economic benefits and efficiencies that come with this formula and now we’re executing to a common plan,” said Dr. Walt Lauderdale, AATS mission director at SSC. “As we move forward together with SpaceX, we’re methodically expanding reuse to leverage the benefits for the USSF and our space vehicle teammates.
“The mission team was able to add the Tranche 0 satellites to USSF-124 in under 30 days, less than six months from the then scheduled launch date. This unprecedented responsiveness is a needed capability for the Space Force to confront today’s threat environment.”
U.S. Air Force + U.S. Space Force announce sweeping changes to maintain superiority
The Department of the Air Force’s senior civilian and military leaders have unveiled sweeping plans for reshaping, refocusing, and re-optimizing the U.S. Air Force (USAF) and U.S. Space Force (USSF) to ensure continued supremacy in those domains while also better posturing the services to deter and, if necessary, prevail in an era of Great Power Competition.

Taken together, the changes made public on February 12th and endorsed by Secretary of the Air Force Frank Kendall, performing the duties of Acting Under Secretary Kristyn Jones, USAF Chief of Staff Gen. David Allvin and Chief of Space Operations Gen. Chance Saltzman, represent one of the most extensive recalibrations in recent history for the USAF and USSF.
“Today, we are announcing 24 key decisions that are going to address the current force and our ability to stay competitive,” Kendall said in announcing the changes and the rationale behind them. “We need these changes now; we are out of time to reoptimize our forces to meet the strategic challenges in a time of Great Power Competition.”
While the changes feature a mix of near-term and longer-term initiatives, senior leaders emphasized the need for speed. “We are out of time,” Kendall said repeatedly in urging action on the changes.
The changes included in the plan are grouped in four main categories – Develop People, Generate Readiness, Project Power, Develop Capabilities — and include…
Develop People
• Consolidate force development functions under an expanded Airman Development Command to provide Airmen a common, mission-focused development and training path.
• Expand technical tracks for officers and create technical tracks for enlisted Airmen; reintroduce warrant officers in IT and Cyber fields to maintain technical leadership in these highly perishable skills.
• Develop “Mission Ready Airmen” with training focused on a mix of skills needed for wartime operational mission readiness.
• Continue to transform leadership development and training at U.S. Air Force Academy, Officer Training School, and ROTC to prepare new officers to effectively lead Airmen and Guardians in the context of Great Power Competition and redesign career paths to produce Guardians that meet our high-tech operational demands.
Generate Readiness
• Reorient Air Combat Command to focus on generating and presenting ready forces to combatant commanders.
• Implement large scale exercises and mission-focused training encompassing multiple operational plans to demonstrate and rehearse for complex, large-scale military operations.
• Incorporate no-notice/limited-notice operational readiness assessments and inspections in the Air Force and Space Force to reflect pacing challenge requirements.
• Restructure key processes related to aviation spares and weapons systems to be data-driven and risk-informed to improve weapon systems health.
• Implement Space Force readiness standards that reflect operations under contested conditions rather than those of a benign environment.
• Conduct a series of nested exercises in the Space Force, that increase in scope and complexity, fit within a broader Department of the Air Force-level framework, and are assessed through a Service-level, data-driven process to measure readiness.
Project Power
• Structure Air Force Operational Wings as mission ready “Units of Action” categorized as Deployable Combat Wings, In-Place Combat Wings or Combat Generation Wings. Each will have its own structure, with a redesigned concept of support for agile combat employment or ACE, to ensure the wings are prepared to execute their missions with assigned Airmen and units.
• Establish the relationship between Combat Wings and Base Command. Combat Wings will focus on mission level warfighting readiness and Base Commands will focus on supporting Combat Wings and operating the base in competition, crisis and conflict.
• Elevate AFCYBER to a standalone Service Component Command, reflecting the importance of the cyber mission to the Joint Force and across the Department of the Air Force.
• Formalize Space Force Combat Squadrons as Units of Action, complete activation of the remainder of Space Force Service Components and accelerate implementation of the Space Force Generation model.
Develop Capabilities
• Create a Department of the Air Force Integrated Capabilities Office to lead capability development and resource prioritization to drive Department of the Air Force modernization investments.
• Combine disparate efforts to create the Office of Competitive Activities to oversee and coordinate sensitive activities.
• Create a Program Assessment and Evaluation Office to foster structure and incorporate a more strategic and analytically based approach to resourcing decisions.
• Establish Integrated Capabilities Command to develop competitive operational concepts, integrated requirements, and prioritized modernization plans to align with force design.
• Create a new Information Dominance Systems Center within Air Force Materiel Command (AFMC) to strengthen and elevate the Air Force’s focus on Command, Control, Communications, and Battle Management; Cyber; Electronic Warfare; Information Systems; and Enterprise Digital Infrastructure.
• Strengthen the support to nuclear forces by expanding the Nuclear Weapons Center to become the Air Force Nuclear Systems Center within AFMC. This will provide comprehensive materiel support to the nuclear enterprise; establish a 2-star general officer as the Program Executive Officer for Inter-Continental Ballistic Missiles.
• Refocus the Life Cycle Management Center within AFMC as the Air Dominance Systems Center to synchronize aircraft and weapons competitive development and product support.
• Establish an Integration Development Office within AFMC to provide technology assessments and roadmaps. It will drive alignment and integration of mission systems across centers and provide technical expertise to assess operational concept feasibility.
• Create Space Futures Command, a new field command, that develops and validates concepts, conducts experimentation and wargames, and performs mission area design.
Viasat’s 1st U.S. Navy Military Sealift Command Ship installation
Viasat, Inc. (NASDAQ: VSAT) has completed the first ship installation for the U.S. Navy Military Sealift Command (MSC) under the Next Generation Wideband (NGW) Follow-On (FO) 10-year, Indefinite Delivery/Indefinite Quantity (IDIQ) contract awarded to Inmarsat Government by the Defense Information Systems Agency (DISA) on June 30, 2022.

Under the contract, the company maintains and operates commercial communications infrastructure, which includes satellite systems, teleport services and terrestrial services. Inmarsat Government is now part of Viasat’s government business, following Viasat’s acquisition of Inmarsat on May 30, 2023. This first installation of 105 ships demonstrates the company’s ability to deliver a robust, reliable global managed satellite communications (SATCOM) solution.
The company upgraded the MSC ship’s primary afloat network from Ku-band to the Global Xpress (GX) Ka-band system and ELERA Enhanced L-band Maritime Antenna (ELMA), a variant of the award-winning, LAISR L-band solution to provide communications on the move via a small-size, high throughput terminal.
The hybrid solution of Ka- and L-band service ensures that the MSC ships have secure, resilient, worldwide communications capabilities, as well as a reliable global, on-demand backup network. This approach is designed to provide significant enhancements over legacy Ku-band by providing higher and scalable data rates on ships’ primary and back-up systems, and uniform coverage across the GX and ELERA networks.

Additionally, by delivering the primary and secondary SATCOM capabilities in a holistic, managed service model that includes satellites, ground networks and type-approved terminals – SATCOM as a Service.
The MSC fleet benefits from an integrated, worldwide solution that delivers high throughput with RF (Radio Frequency) band and path diversity to ships at sea.
All of the network aspects are designed as a single solution and for mobility, so users experience a reliable, on-demand continuous service.
Voyager Space + Palantir to advance national security capabilities
Voyager Space (Voyager) has signed an MOU) and teaming agreement with Palantir USG, Inc. that is focused on exploring and enhancing national security capabilities within the commercial space domain.
Palantir provides adaptable software solutions and architectures to ensure the resilience, effectiveness, and availability of U.S. defense and space capabilities.
The collaboration between Voyager and Palantir will center around the joint exploration of cutting-edge Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) capabilities, aimed toward technology demonstration missions on the International Space Station and the future Starlab commercial space station.
As part of the agreement, Voyager and Palantir will explore the integration of Palantir’s AI / ML and edge processing capabilities to support Starlab station development, manufacture, and future operations.

Sample use cases include space domain awareness (SDA), data fusion, and processing at the edge to enable autonomous decisions and secure collaboration with Allies.
The collaboration extends beyond the two companies, as both parties will actively identify opportunities for cooperation with other national security stakeholders. This includes government agencies, working groups, commercial partners, or partner nations, such as NATO or Five Eyes countries.
“This alliance represents a shared commitment to advancing the frontiers of global commerce, civil, and national security capabilities, reaffirming the critical role industry has to bring leading-edge technology to the evolving landscape of space exploration and security,” said Shyam Sankar, CTO of Palantir. “The opportunity to partner with Voyager will set the stage for collaboration across the ecosystem of leading technology firms dedicated to this mission,” Sankar added.
“This strategic collaboration signifies a major milestone in harnessing the combined expertise of Voyager and Palantir to elevate space domain security,” said Marshall Smith, CTO of Voyager.


