AFSPC-6 Climbs To Sensitive Orbit
A United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta IV rocket that carried the AFSPC-6 mission for the United States Air Force lifted off from Space Launch Complex-37 on August 19th at 12:52 a.m. EDT—this was ULA’s seventh launch in 2016 and the 110th successful launch since the company was formed in December of 2006.

“Thank you to the ULA, Air Force and industry partners for the outstanding teamwork and flawless execution that made today’s mission a success,” said Laura Maginnis, ULA vice president of Custom Services. “This morning’s AFSPC-6 launch is a prime example of why our customers continue to place their trust us to launch our nation’s crucial space capabilities.”
This mission was launched aboard a Delta IV Medium+ (4,2) configuration Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle (EELV) powered by one common booster core. The common booster core was powered by an RS-68A liquid hydrogen/liquid oxygen engine producing 702,000 pounds of thrust. A single RL10B liquid hydrogen/liquid oxygen engine powered the second stage. The booster and upper stage engines are both built by Aerojet Rocketdyne. ULA constructed the Delta IV Medium+ (4,2) launch vehicle in Decatur, Alabama.
The AFSPC-6 mission consists of twin Geosynchronous Space Situational Awareness Program (GSSAP) spacecraft, built by Orbital ATK. The new satellites will join the first two GSSAP spacecraft launched approximately two years ago aboard a Delta IV launch vehicle.
GSSAP is a space-based capability that collects space situational awareness data, allowing for more accurate tracking and characterization of man-made orbiting objects. There is a clear, unobstructed and distinct vantage point for viewing resident space objects orbiting Earth in a near-geosynchronous orbit without the weather or atmosphere disruptions that limit ground-based observations.
The data from GSSAP greatly improves the ability to rapidly detect, warn, characterize and attribute disturbances to space systems in the geosynchronous environment.
The EELV program was established by the US Air Force to provide assured access to space for Department of Defense and other government payloads. The commercially developed EELV program supports the full range of government mission requirements, while delivering on schedule and providing significant cost savings over the heritage launch systems.

A ULA Delta IV rocket awaits the launch command at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Space Launch Complex 37. Photo is courtesy of United Launch Alliance.
"Today's successful launch will enhance our capabilities in space situational awareness and our space-based space situational awareness architecture," said Lt. Gen. Samuel Greaves, SMC commander and Air Force program executive officer for space. "We will continue our unwavering focus on mission success and guaranteeing assured access to space for our nation. Congratulations to the AFSPC-6 integrated team and all mission partners on a successful launch."
The satellites join a GSSAP constellation currently supporting US Strategic Command space surveillance operations as a dedicated Space Surveillance Network sensor.

Photo captured from the AFSPC-6 launch infocast, courtesy of ULA.
The GSSAP also supports the Joint Functional Component Commander for Space by collecting space situational awareness data, allowing for more accurate tracking and characterization of man-made orbiting objects.

Air Force Space Command's Space and Missile Systems Center, located at Los Angeles Air Force Base, California, is the US Air Force's center of acquisition excellence for acquiring and developing military space systems. SMC's portfolio includes the Global Positioning System (GPS), military satellite communications, defense meteorological satellites, space launch and range systems, satellite control networks, space based infrared systems and space situational awareness capabilities.
Additionally, the 45th Space Wing supported this successful launch of the third and fourth Orbital ATK-built Geosynchronous Space Situational Awareness Program satellites for the US Air Force with weather forecasts, launch and range operations, security, safety and public affairs. The wing also provided its vast network of radar, telemetry and communications instrumentation to facilitate a safe launch on the Eastern Range.
www.ulalaunch.com
Goodbye GPS SVN-23... Satellite Heads To Higher Orbit
The USAF's 2nd Space Operations Squadron bid goodbye to Global Positioning System Satellite Vehicle Number 23 via final command and disposal at Schriever Air Force Base, Colorado, on August 26, 2016.

Older, less capable satellites, such as SVN-23, are moved into a disposal orbit at end of life to reduce risk to the GPS constellation, and to create space for more satellites.
As GPS satellites do not carry the amount of fuel required for de-orbit maneuvers, they are instead pushed to a higher orbit, roughly 1,000 kilometers above the operational GPS orbit.
SVN-23 has a unique story, as its journey of almost 26 years came with a rough beginning—it severely malfunctioned in its initial orbit. 2 SOPS contractors Bruce Carlson and Mike O’Brine were on the operations floor when the satellite’s solar array stopped working.
At the time, the operators realized the design flaw in the vehicle. If they did not correct the malfunction, SVN-23 would have additional failures, which could actually endanger their ability to dispose of it.
In 2005, a decision was made to allow normal operations on the B side of the solar array drive and miraculously it worked for the remaining 11 years of life on the vehicle.
The extra care and diligence with SVN-23, through hundreds of operators and contractors, sustained the 25-year-old satellite’s life to the final command Friday, a bit of a marvel, since the design life of the spacecraft was only supposed to be 7.5 years.
The team had to switch the solar array’s mode to the second drive motor to save the vehicle’s life.
Capt. Aaron Blain, 2 SOPS DOA (analysis) flight commander, said that this is actually a story of the men and women who’ve been keeping these vehicles alive much longer than expected.

Photo: Lt. Col. Peter Norsky, 2 SOPS commander, encourages his team on the operations floor during the final command ceremony of Global Positioning System Satellite Vehicle Number 23 at Schriever Air Force Base, Colorado, Friday, August 26, 2016. Norsky insisted the survival of the “bird” was because of the space operator crews who man their stations 24 hours a day, 365 days a year. Photo is courtesy of the US Air Force photo and 2nd Lt. Darren Domingo.
The launch occurred on the 26th of November in 1990 and early orbit operations were completed in the early part of December. The satellite was stabilized and, 12 hours later, the A side of the solar array drive failed.
According to Bruce Carlson, the crew asked, hey, what's up with this, and the reply was "Oh, it looks like the solar array appears to have failed to power off conditions. We’ll just power it back on and it will come back on. Oh wait, it didn’t." That was a fun day or two when that happened, he added.
O'Brine commented that for the next 14 years, twice per orbit, a technique was run called scissoring, where (during) orbit dawn and orbit dusk, the solar arrays were manually commanded back and forth, all from a ground command.
Lt. Col. Peter Norsky, 2 SOPS commander, said, “This is just an incredible event and I’m really proud that you all have put so much into (SVN-23) and every single one of our birds. Having something last this long is truly a testimony to (our) operations. Every single day that you are all on the ops floor, you’re contributing to things like this, so thank you for what you do.”
Story by 2nd Lt. Darren Domingo, 50th Space Wing Public Affairs, USAF
Russia Jamming Up The Works
In a story posted at Sputnik News, Russia has now developed a system that can block enemy electronics.
The report states that an integrated jamming system to screen strategic facilities from cruise missiles, smart bombs and drones using GPS, GLONASS, Galileo and Beidou global positioning systems for homing, has entered service with the Russian armed forces.
This was originally reported in the Russian newspaper Izvestiya—they cited a Defense Ministry source in Moscow.
Dubbed as POLE-21, the system consists of jamming modules installed on mobile phone towers that operate as a single whole to cover entire areas, making them impregnable to satellite navigation systems.
In addition to be being powered by a tower’s circuit, the Pole-21 modules also use their GSM antennas as a backup channel for signal control and transmission.
“The system has already been successfully tested and is now operational,” the source told the newspaper.
All of the four global positioning systems whose signals are effectively deflected by Pole-21 work within the 1176.45 and 1575.42 MHz range.
Even a 20 watt transmitter is enough for Pole-21 to jam all signals in this range within a radius of 80 kilometers.
Pole-21 has one downside, however; while generating radio interference against the enemy using the GPS satellite navigation systems, the system also affects the domestic users of GPS and the Russian GLONASS.
Real-Time Info Access For DoD End-Users From SES
A satellite beam operating at less than 200 milliseconds per round trip, a full duplex symmetric 155 Mbps link, gateway access, a transportable 2.4 meter AvL terminal, terrestrial backhaul, installation services and 24x7x365 operations and maintenance activities, that's what SES Government Solutions (SES GS) will provide to a US DoD end-user via a new contract.
SES S.A. has revealed that SES Government Solutions (SES GS), a wholly owned subsidiary of SES, has been awarded this contract to provide an O3b Networks high throughput, low latency satellite communications solution for the government customer.
The contract also enables the US Government to order additional O3b services to meet surge requirements.
Operational benefits of the solution include the capability to transfer large files from remote locations in just minutes instead of hours.
Cloud-based applications and information can be used nearly anywhere in the service area. End-users will be able to view simultaneous high definition (HD) videos providing situational awareness to commanders.
This real-time information access may enable better-informed, life-saving decisions in the field.
This is SES GS’ second US Government customer to use O3b Networks’ services this year.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) was the first US Government agency to sign an agreement with SES GS, that one for an O3b high throughput solution at the Pago Pago National Weather Service Office in American Samoa. This service has been delivering critical information since May of 2016.
According to Pete Hoene, the President and CEO of SES GS, with SES’s recent acquisition of O3b, the company is uniquely positioned to offer scalable, game-changing Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) high throughput, low latency and global Geosynchronous Earth Orbit (GEO) communications products and solutions. This is a clear differentiator for SES GS and the firm's US Government customers.
www.ses-gs.com/
ViaSat To "Pump Them Up"
ViaSat must have been on the US Navy's 'radar' when the Space and Naval Warfare Systems Command (SPAWAR) recognized ViaSat Inc.'s expertise and awarded them a sole source contract for engineering, technical services and hardware/software products in support of the US Navy’s joint Ultra High Frequency (UHF) military satellite communications (satcom) system.

Under this SPAWAR contract, ViaSat will help support the sustainment and modernization of the joint UHF military SATCOM network integrated control system, UHF satcom channel controllers and user terminals.
In addition, ViaSat will provide a path to a modern crypto design for next-generation UHF terminals.
This award highlights the US Government’s commitment to maintaining the long-term viability of proven UHF systems; ensuring Navy warfighters have ongoing support and access to proven communications technology when in the battlespace.
Ken Peterman, Senior Vice President and General Manager, Government Systems Division, ViaSat said in an interview, “UHF military SATCOM has a long history enabling beyond line-of-sight communication across the battlespace, and provides a solid, ‘always available’ communications solution.
"This award reflects the Navy’s commitment to using proven UHF radios and channel controllers already deployed worldwide, mitigating risk with non-fielded communications systems in order to ensure continued and enhanced capabilities for the warfighter many years into the future.”
CPI's ASC Signal Division Sees Their Spira-Cone™ Heading To Indonesia
An antenna that does its job is invaluable and in demand, which has been proven most recently by the ASC Signal Division of Communications & Power Industries LLC's (CPI) with their high-frequency (HF) unit.
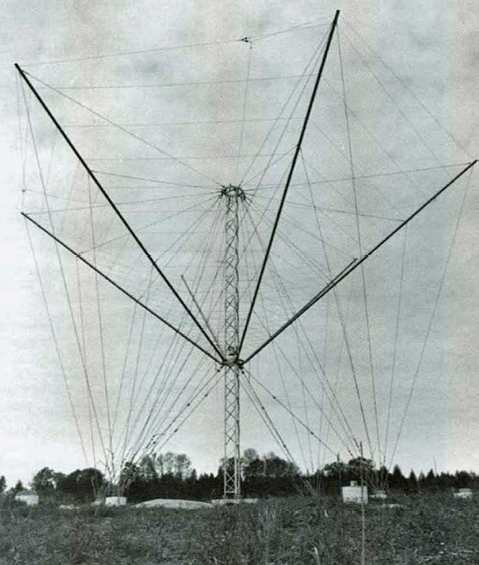
CPI's ASC Signal Division Type 3000 Series GRANGER™ HF Broadband Multi-Mode SPIRA-CONE® antennas.
ASC Signal has been awarded a contract for four Model 3005 Spira-Cone™ HF antennas in Indonesia by Pratama Wahyu Teknik (PWT), a communications systems integrator headquartered near Jakarata.
Model 3005 HF antenna system was first developed to meet a requirement by the US Navy for a low-profile antenna to replace older, rotatable log-periodic antenna systems. This model includes mode voting technology, which is widely used in non-commercial HF systems, and extends the use of that technology into the commercial sector.
PWT will use the Model 3005 Spira-Cone™ HF antennas for air-to-ground communication and navigation purposes for the Indonesian National Directorate General of Civil Aviation for RDARA, the Regional and Domestic Air Route Area coverage agency in Makassar and Merauke, Indonesia.
Although this is CPI ASC Signal Division's first project for PWT, the new contract is not its first project in Indonesia nor the region as they have been supplying antenna systems to the Southern Pacific region for approximately 12 years.
Their projects include the provision of state-of-the-art antenna products to Australian aviation authorities and the Indonesian military through large, multi-national original equipment manufacturers.
Keith Buckley, president of CPI ASC Signal Division commented, "The Southern Pacific region relies heavily on air transportation for a variety of its social and economic needs, and it is vital that it has access to reliable, proven technology for aviation communications and navigation applications.
"CPI ASC Signal Division's HF antenna systems are trusted components of aviation systems throughout the region. We are honored that Pratama Wahyu Teknik, a world-class integrator, has recognized our Model 3005 technology as optimal for its system needs in Indonesia, and we look forward to a productive relationship."
www.cpii.com/ascsignal
www.pratamateknik.com
OnePath Is On The Correct Path
Harris CapRock Communications answered the growing demand for bandwidth in the cruise, energy and commercial maritime industries with the launch of its OnePath long-range wireless radio.

This radio provides a unique mode of complementary connectivity to Very Small Aperture Terminal (VSAT) technology and provides higher throughput and increased redundancy.
The radio enables a fully secure, localized wireless data/voice network complete with traffic management. OnePath provides first/last mile connection and can close links in excess of 160 km with appropriate heights and the radio is equipped with operating modes for Point-to-Point and Point-to-Multi-Point applications.
Licensed or unlicensed spectrum options are available, with throughputs of up to 400 mbps. OnePath features:
• Data rates of greater than 400 Mbps
• Reaches distances of 160 km or more
• Embedded or external device encryption for security
• Web-based user interface for configuration & monitoring
• Multiple links can be bonded for additional coverage
Matthew Broida, vice president, marketing, Harris CapRock, said, “The OnePath radio solution offers bestin- class throughput performance and spectrum efficiency and is lightweight, rugged and easy to deploy. It offers extremely low latency to ensure rapid delivery of high bandwidth applications including VoIP, real-time video, teleconferencing and sensor traffic.”
The OnePath radio offers a robust, always-on communications experience delivered by a secure, optimized network that is supported by a worldwide, redundant infrastructure.
www.harriscaprock.com/onepath-radio/






