Going… Going… Great! The USSF’s GPS III SV05 Satellite Experiences A Successful SpaceX Falcon 9
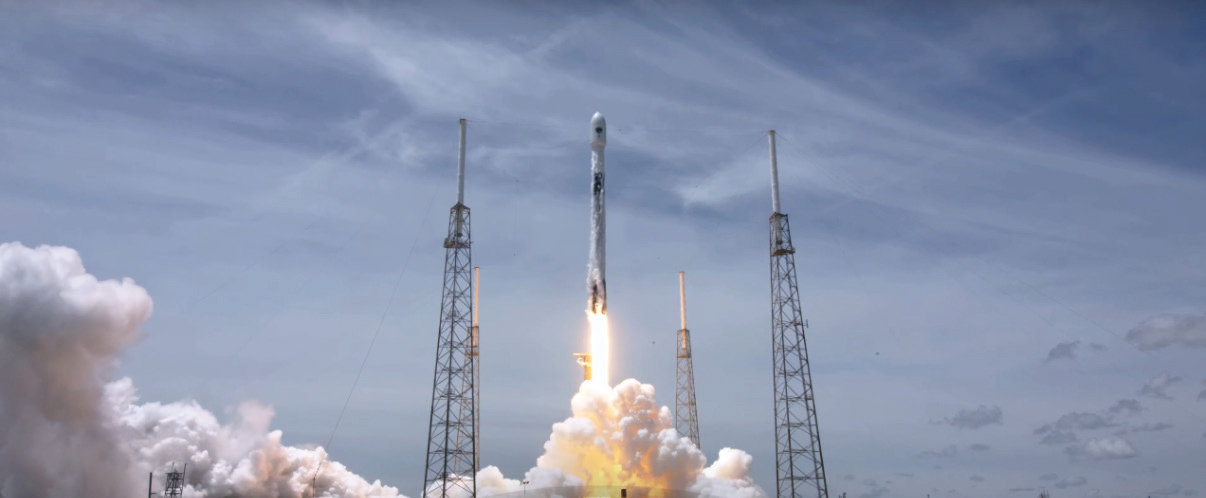

The Falcon 9 liftoff of the GPS III SV05 satellite
from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. Screen
capture is from the SpaceX live stream
of the launch.
Push To Orbit
On June 17, SpaceX successfully launched the upgraded Global Positioning System (GPS) satellite into orbit for the U.S. Space Force (USSF).
The flight — the 19th launch this year for SpaceX and its workhorse Falcon 9 rocket — lifted off from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station during a 15-minute window that opened at 12:09 p.m. EST (1609 GMT). Perched atop the rocket is the GPS III-SV05 satellite, which was built by Lockheed Martin.
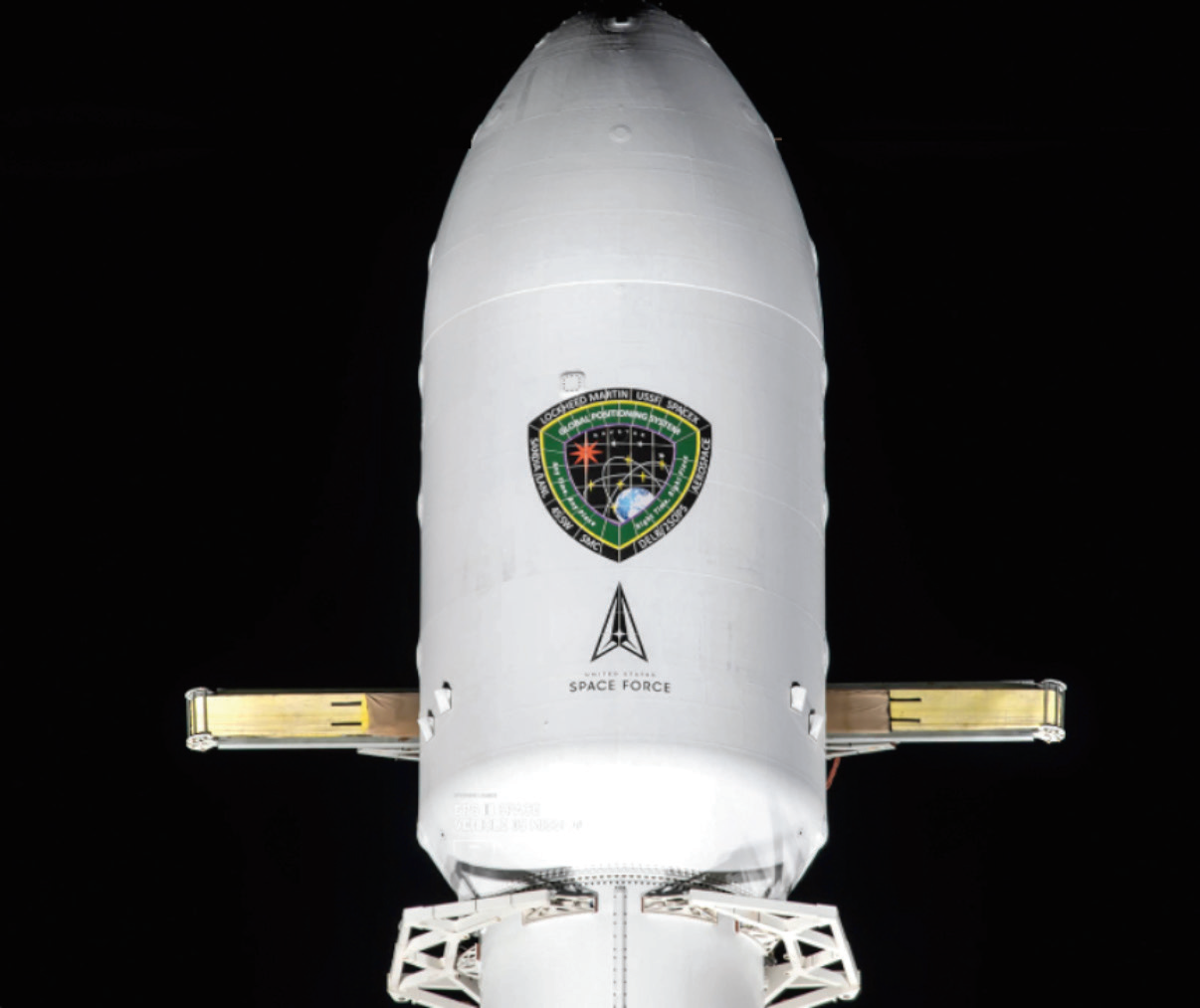

This is the fifth launch of an upgraded, next-generation, GPS III satellite to date. Built by Lockheed Martin in Colorado, these upgraded GPS satellites are some of the most sophisticated spacecraft ever built.
They’re equipped with anti-jamming capabilities that are more robust than previous iterations and more powerful signals for increased accuracy, according to Lockheed Martin representatives.

GPS III SV05 @ Lockheed Martin prior to
shipment to Cape Canaveral AFS.
GPS III SV05 is the 24th Military Code (M-Code) signal-enabled, GPS space vehicle on-orbit, completing the constellation’s baseline requirement to provide the nation’s military forces a more-secure, harder-to-jam and spoof GPS signal.
This launch featured the fifth in a series of ten, upgraded, GPS III satellites for the military that will join the current constellation of satellites already on-orbit.
These crucial satellites help to provide positioning, navigation and timing services for more than four billion users worldwide. GPS III-SV05 will replace an aging predecessor that was launched two decades ago.
Last year, Space Force officials announced that the U.S. military had granted SpaceX permission to launch national security payloads on previously flown rockets. That news followed on the heels of another recent decision to allow SpaceX to recover the first stages of Falcon 9 boosters used on national security missions, something that was previously not allowed.

Screen captures are from the SpaceX live stream
of the launch and shows the droneship before and
after the Falcon 9 first stage completes a
successful landing.
This mission was the first to fly on a veteran Falcon 9. After ferrying the GPS satellite into space, the rocket will then land back on Earth on a floating platform at sea, the “Just Read the Instructions” droneship. The star of this mission is a previously flown Falcon 9 first stage, known as B1062 to SpaceX.This first stage is embarked on its second mission, after lifting another GPS satellite last year.
The current GPS constellation is composed of 31 operational spacecraft. GPS satellites operate in Medium Earth Orbit (MEO) at an altitude of approximately 20,200 km (12,550 miles) in six orbital planes. Each satellite circles the Earth twice per day. This latest generation of GPS satellite boasts a 15 year design life, which per day. This latest generation of GPS satellite boasts a 15 year design life, is 25 percent longer than the previous generation of GPS satellites on-orbit.
• Three times better accuracy
• Up to eight times improved anti-jamming capabilities
• A new L1C civil signal, which is compatible with international global navigation satellite systems, like Europe’s Galileo, to improve civilian user connectivity.
About 90 minutes after liftoff, U.S. Space Force and Lockheed Martin engineers at the company’s Denver GPS III Launch & Checkout Operations Center declared GPS III SV05 separated from its SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket and “flying” under their control.
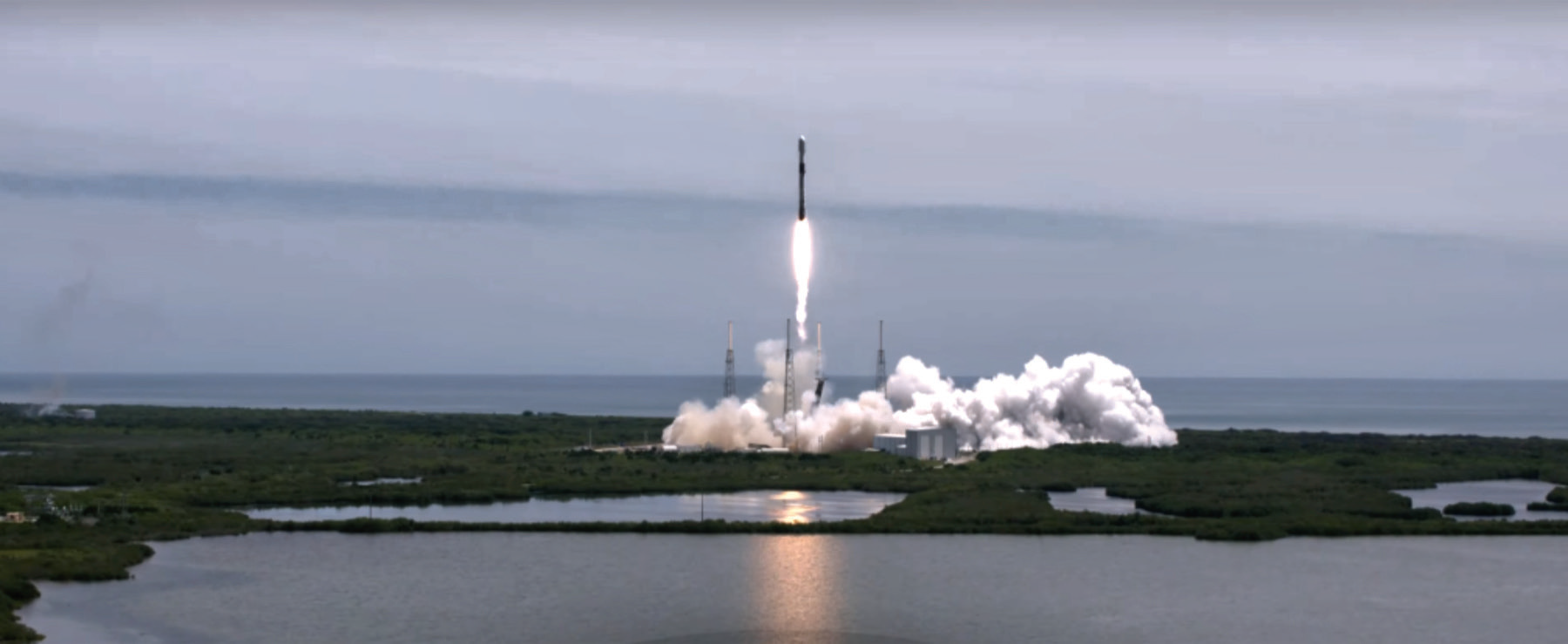

Over the next several days, GPS III SV05’s onboard liquid apogee engine continued to propel the satellite toward operational orbit. After arrival at the designed slot, engineers sent the satellite commands to deploy solar arrays and antennas and prepare GPS III SV05 for handover to Space Operations Command.
Part of U.S. critical national infrastructure, GPS drives an estimated $300 billion in annual economic benefits and is responsible for $1.4 trillion since its inception. Globally, more than 4 billion military, civil and commercial users depend on GPS’ positioning, navigation and timing signals.
Lockheed Martin is part of the GPS III team led by the Space Production Corps Medium Earth Orbit Division at the U.S. Space Force’s Space and Missile Systems Center, Los Angeles Air Force Base. The GPS Operational Control Segment sustainment is managed by the Enterprise Corps, GPS Sustainment Division at Peterson Air Force Base. The 2nd Space Operations Squadron, at Schriever Air Force Base, manages and operates the GPS constellation for both civil and military users.
“With GPS III SV05, we continue our focus on rapidly fielding innovative capabilities for the Space Force’s Positioning, Navigation and Timing Mission,” said Tonya Ladwig, Lockheed Martin vice president for Navigation Systems. “With each satellite we bring to orbit, we help the U.S. Space Force to modernize the GPS constellation’s technology and to imagine future capability. Our next three satellites, GPS III SV06, SV07 and SV08, are already complete and just waiting for a launch date.“
“We are building on the successful booster recoveries of GPS III-3 and GPS III-4 last year and making a historic step with the GPS III-5 mission using a previously flown vehicle,” said Colonel Robert Bongiovi, Launch Enterprise director.
“The affordability and flexibility provided with SpaceX’s reused launch vehicles open additional opportunities for future NSSL missions and provide our nation’s warfighters with the advanced capabilities they need.”
“The GPS III program office, in partnership with our contract teammate,s continues to push the envelope on the capabilities they deliver to users, both civil and military around the globe,” said Mr. Cordell DeLaPena, Jr., U.S. Space Force program executive office for Space Production. “Our latest GPS III satellites’ nearly 70 percent digital payload provides the Space Force with greater operational flexibility, as well as cutting edge capabilities while continuing to support legacy users. Fueled off the success of our latest GPS III SV04 launch, I look forward to the successful launch of SV05 just 7 months later.”
“Our GPS program team overcame numerous challenges presented by the COVID-19 pandemic to safely and successfully launch GPS III SV04. Their resilience and ingenuity validated a new concept of operations which has paved the way for the launch of GPS III SV05 just seven months later,” said Colonel Edward Byrne, MEO Space Systems Division chief. “SV05 will continue to modernize our GPS constellation by increasing our capabilities with advanced features for both our civil and military users across the world.”
The Space and Missile Systems Center, located at Los Angeles Air Force Base in El Segundo, California, is the U.S. Space Force’s center of acquisition excellence for acquiring and developing military space systems. Its portfolio includes the development of advanced space and launch capability and systems, global positioning systems, military satellite communications, defense meteorological satellites, space launch and range systems, satellite control networks, space-based infrared systems, and space situational awareness capabilities.
Northrop Grumman Successfully Launches USSF / SMC’s TacRL-2 Payload
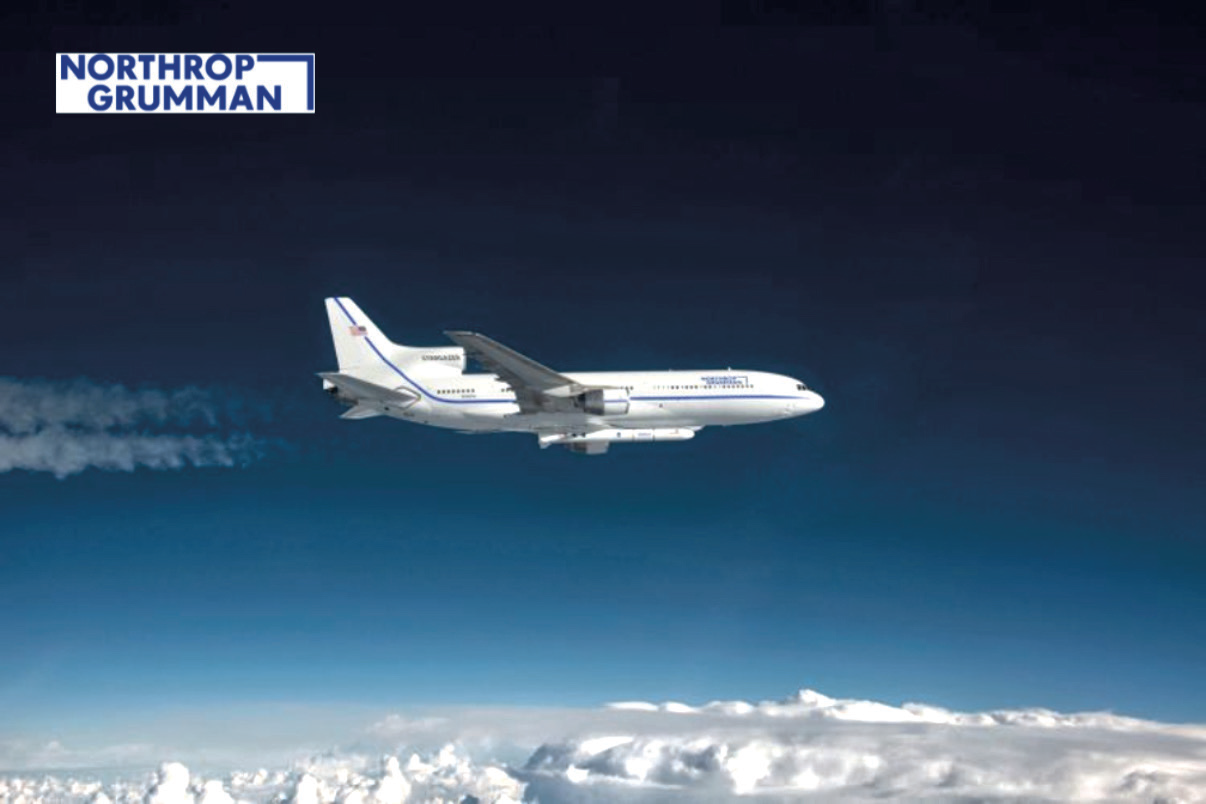

Northrop Grumman successfully launched the TacRL-2 payload into orbit for the U.S. Space Force’s Space and Missile Systems Center using the company’s Pegasus XL rocket.
Pegasus, the world’s first privately-developed commercial space launch vehicle, is an air-launched, three-staged rocket carried aloft by Northrop Grumman’s specially modified “Stargazer” L-1011 aircraft.
U.S.A.F. ISR Prime Contract Issued to Leidos

Leidos (NYSE: LDOS) has been awarded a prime contract by the U.S. Air Force to provide solutions for a broad spectrum of aviation requirements. Leidos will support the Air Force’s Intelligence Surveillance Reconnaissance & Special Operations Forces (ISR/SOF) Directorate (WI), Sensors Division (WIN) Non-Standard Foreign Military Sales (FMS) branches. The multi-award, indefinite delivery/indefinite quantity contract has a total estimated value of $950 million. The period of performance for the contract is 13 years total, with a 10-year ordering period and an additional 3 year performance period. Work will be performed at locations worldwide.
The Leidos team will bring a cadre of professionals and tools from across the industry to improve both U.S. and allied ISR capabilities. Leidos will also provide full aircraft and ISR sensor integration, procurement of hardware and spares, sustainment support and inspections for airworthiness/configuration. ISR/SOF provides support to all weapons systems in its portfolio. The ISR functions are principal elements of America’s defense capabilities. They include a wide variety of systems for collecting, processing and disseminating intelligence for national security decision makers and military commanders.
“This award underscores Leidos’ strong performance leveraging decades of operation and technical integration expertise for the Air Force,” said Mike Chagnon, Leidos Senior Vice President and Operations Manager. “We look forward to supporting the Air Force and its mission to maintain multi-domain dominance.”
Iridium Receives An R&D Contract From The U.S. Army
Iridium Communications Inc. (NASDAQ: IRDM) has been awarded a research and development contract worth up to $30 million by the United States Army to develop a payload to be hosted on smallsats that support navigation systems, guidance and control for the global positioning system (GPS) and GPS-denied precision systems— the new experimental Iridium payload is intended to be hosted by another LEO commercial satellite constellation, complementing the Iridium® constellation’s capabilities.
Through this contract, the Army intends to develop this payload to support the concept of a rapidly deployable smallsat constellation to provide more effective sensor-to-soldier data transmission when in the field. The development of this new payload is based on Iridium Burst® technology, a service that can transmit data to millions of enabled devices at a time from space.
The U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) and Iridium have partnered for more than 20 years, with hundreds of thousands of U.S. government subscribers using Iridium push-to-talk (PTT), voice, IoT, L-band broadband and Iridium Burst services. The continuing growth in adoption of Iridium services also brings increased collaboration between the government and Iridium’s ecosystem of partners, that bring their knowledge to help further complement and advance the DoDs SATCOM capabilities. For this contract, Iridium partners Satelles and SEAKR will bring their expertise as subcontractors to assist with development.
This research and development project was enabled through an “Other Transaction Agreement” (OTA) in support of the Army and was entered into between Advanced Technology International (ATI) and Iridium under the authority of the Aviation and Missile Technology Consortium (AMTC). The OTA was developed through the authority of the Department of Defense to carry out these types of prototype projects and to further streamline the process for adopting new technology solutions from various industries.
“Iridium has always been focused on providing innovative, reliable and high-value services to the U.S. warfighter,” said Scott Scheimreif, executive vice president, government programs, Iridium. “This program can help add to warfighter readiness to conduct a full range of military operations at a tactical level. This includes the ability to enhance effectiveness of military units, weapons and equipment during combat against near-peer adversaries.”

“This is one of the largest engineering contracts in Iridium’s history, and we’re pleased to once again bring the value of Iridium and our partner ecosystem to the fore at the request of the United States Army,” said Matt Desch, CEO, Iridium. “It also represents another phase in the evolution of our growing relationship with the DoD, and we’re excited to engage on this experimental multi-constellation adaptation of our service.”
Shortly after the rocket’s release from Stargazer, at approximately 40,000 feet above the Pacific Ocean, Pegasus ignited its first stage, beginning its successful flight carrying TacRL-2 to its intended orbit.

This is the 45th successful launch of Pegasus, which uses solid propulsion to offer maximum responsiveness by enabling launch to a wide variety of orbits on short timelines. This capability provides customers with the flexibility to operate from virtually anywhere on Earth with minimal ground support requirements.
Pegasus has launched more than 90 satellites into LEO from five separate launch sites in the United States, Europe and the Marshall Islands.
“This Pegasus launch was a clear demonstration of our team’s ability to provide rapid and responsive operation needs,” said Rich Straka, vice president, launch vehicles, Northrop Grumman. “Our team was able to execute the design, integration and testing of the TacRL-2 launch vehicle in less than four months from contract award.”
Acquisition: General Atomics Imports Synopta Into Their Operations

General Atomics (GA) has acquired Synopta GmbH, a leader in the development and production of complex opto-electronic instrumentation for space and terrestrial applications.
Founded in 2004 in Eggersriet, Switzerland, Synopta develops opto-electronic instrumentation and provides strategic and technical consultancy services. Synopta’s customers include a wide range of European organizations, national agencies, and international corporations active in the fields of defense, space and capital goods.

“Synopta’s pioneering expertise and innovative developments in communication, beam control, pointing assemblies, and stationary and transportable optical ground systems will supplement the diverse portfolio of laser communications, sensors, and ground systems which enable delivery of dependable solutions to government and other customers,” said Scott Forney, President of General Atomics Electromagnetic Systems Group. “Synopta will continue to serve its European customer base but will expand now also to customers in the United States and other countries, while contributing to GA’s systems and strategic objectives. Under its new name General Atomics Synopta GmbH, the company will form a technical center of excellence within the General Atomics group of companies.”
“We are excited about the perspectives resulting from this acquisition. While continuing to operate in the Canton of St. Gallen as a Swiss company, we now have the opportunity to demonstrate the potential of true transatlantic co-operation in the hi-tech field,” said Jens Kunde, General Manager of GA Synopta.
Northrop Grumman Demonstrates Advanced Networking at Northern Edge 2021

During the Northern Edge 2021 joint exercise, Northrop Grumman Corporation (NYSE: NOC) successfully demonstrated advanced communications and networking systems technology to connect warfighters in contested environments.

LITENING is an electro-optical infrared sensor
system for targeting and surveillance that enables
aircrews to detect, acquire, identify and track targets
at long ranges. LITENING enables a wide range of
missions, including precision targeting, close air
support, intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance,
and humanitarian assistance
Validated on three separate platforms, one demonstration was conducted in partnership with the Air National Guard and involved the company’s Freedom Pod — a derivative of the LITENING advanced targeting pod that incorporates a Freedom Radio and an infrared search-and-track sensor for passive surveillance and targeting.

F-15 Eagles and Strike Eagles from the 53rd Wing
and 96th Test Wing sit on the ramp at Joint Base
Elmendorf-Richardson, Alaska during exercise
Northern Edge 21. Approximately 15,000 U.S.
service members participated in the joint training
exercise hosted by U.S. Pacific Air Forces.
The exercise
was conducted on and above the Joint Pacific
Alaska Range Complex, the Gulf of Alaska, and
temporary maritime activities area. U.S. Air
Force photo by 1st Lt. Savanah Bray.
“Northrop Grumman’s Freedom Pod provides swappable, multi-function capabilities to a range of aircraft, including unmanned, to provide a greater level of sensing and connectivity for the warfighter,” said James Conroy, vice president, navigation, targeting and survivability, Northrop Grumman.
Northrop Grumman’s advanced networking technologies, including the Freedom Radios and Freedom Pods showcased at Northern Edge, help warfighters and branches of the military easily communicate and securely share actionable information across air, land, sea and space. The company’s advanced networking technologies are designed to interconnect the missions of today and will provide the functionality needed to support the network-centric operations of tomorrow.
In addition to Freedom Pod efforts, other variants of Northrop Grumman’s Freedom Radios, which enhance situational awareness for a range of manned and unmanned aircraft, were involved in two platform demonstrations centered on advanced 5th generation communications. These demonstrations leveraged the Freedom Radios’ cyber-secure, software-defined, multifunction, open architecture solutions designed to support a wide range of integrated communications and networking capabilities across multiple domains.
“The Freedom Radio product line enhances situational awareness for a range of manned and unmanned aircraft—through 5th generation communications capabilities,” said Jenna Paukstis, vice president, communications solutions, Northrop Grumman. “We have the capabilities needed to connect advanced platforms with functionality necessary to adapt to emerging all-domain mission demands to help the DOD realize its vision for JADC2.”
“Northern Edge is an essential event for operational tests,” said Col. Ryan Messer, 53rd Wing commander. “It is one of only a handful of exercises that combine great power competition-level threat complexities with the joint interoperability necessary to realistically inform our test data. The individuals in the 53rd Wing continue to inspire me with how they challenge themselves and their programs in complex environments, ensuring we deliver the most lethal, ready and capable force for our nation.”
Northrop Grumman has participated in every Northern Edge exercise over the last decade.
Million$$$ Contract For Gilat Satellite Networks For APAC MILSATCOM Customer

Gilat Satellite Networks Ltd. (Nasdaq: GILT, TASE: GILT) has been awarded a multi-million-dollar contract to provide satellite communication (SATCOM) equipment to a large system integrator for a company customer in Asia.
Gilat’s SkyEdge II-c, Capricorn VSATs and TotalNMS will serve the needs of the defense forces to provide tactical SATCOM solutions for mobile platforms and enable efficient communication channels during emergency and disaster response besides the critical C4I needs.
Multiple hubs and hundreds of VSATs will be deployed in redundant configurations to meet the critical security needs, as well as the high quality and key regulatory requirements.
“Gilat was chosen to answer the defense needs due to Gilat’s superior technology, highly secure solution, proven global track record and commitment to the local market,” said Vinod Kaul, General Manager, South Asia, at Gilat. “Together with the local partners we see a large potential for our technology in additional Defense projects, as well as other segments such as Education, Banking, Oil & Gas and IFC.”
“We are proud that Gilat’s SkyEdge II-c platform answers the most stringent requirements and thus provides the technological capability to enable realizing today’s demand of digital warfare, wherever and whenever digital information is required,” said Res. BG. Eyal Zelinger, Gilat’s Vice President of Defense. “This contract is an additional significant step in implementing Gilat’s strategy in the global Defense market.”
USSF’s SMC Transfers Satellite Control Authority For GPS III SV 05 To 2nd Space Ops

Artistic rendition of the GPS III SV 05 satellite
on-orbit. Image is courtesy of Lockheed Martin
The United States Space Force’s Space and Missile Systems Center has transferred Satellite Control Authority (SCA) of the Global Positioning System III Space Vehicle 05 to the 2nd Space Operations Squadron, Schriever Air Force Base. Less than one day after SCA, on June 29, 2021, GPS III SV05 received Operational Acceptance approval, marking the first GPS III SV to receive SCA handover and Operational Acceptance within 24 hours and decreasing the time from launch to on-orbit operational capability by 97 percent and expediting delivery of GPS capabilities to the warfighter.
The partnership with Lockheed Martin and confidence in the GPS III SV design has enabled near, real-time delivery, thanks to the collaboration and integration between the acquisition team, industry, and the operational community.
In 2020, the GPS enterprise launched two GPS III SVs in the midst of a global pandemic. Despite the challenges presented by this pandemic, the enterprise continued to streamline the process from launch to Operational Acceptance by continuously shrinking the delivery timeline.
The innovation and teamwork across the GPS enterprise has enhanced the rapid identification and elimination of redundant on-orbit verification steps.
SV05, nicknamed “ARMSTRONG,” was launched on a SpaceX Falcon 9 Block 5 vehicle on June 17, 2021. This marks the first National Security Space Launch on a previously-flown Falcon 9 booster. In fact, SV05 reused the same booster that delivered GPS III SV04 to orbit in November of 2020.
GPS III SV05 is joining the GPS positioning, navigation, and timing constellation of 31 operational satellites.
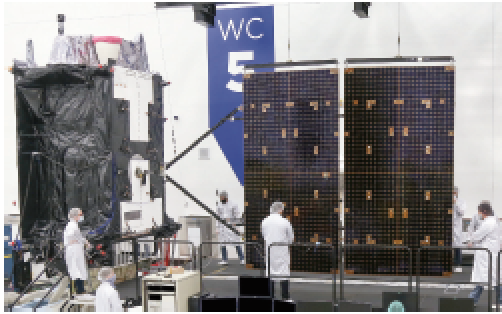
GPS III Space Vehicle 05 in Highbay at Lockheed
Martin. Photo is courtesy of the company.
The Lockheed Martin-built GPS III SVs provide improved accuracy, advanced anti-jam capabilities, and increased resiliency for the GPS constellation and the 4 billion users worldwide. GPS III SV05 will be set healthy to all global users in September 2021, following the completion of on-orbit testing.
“The inclusion of GPS III SV05 into the operational constellation marks another significant milestone for the enterprise with 24 M-Code capable satellites,” said Colonel Heather J. Anderson, Transition Director.
The SpaceX Falcon 9 liftoff of the GPS III SV 05.
Artistic rendition of the GPS III SV 05 satellite on-orbit. Image is courtesy of Lockheed Martin Artistic.



